Emerging strategies for engineering Escherichia coli Nissle 1917-based therapeutics
- PMID: 35232591
- PMCID: PMC9378478
- DOI: 10.1016/j.tips.2022.02.002
Emerging strategies for engineering Escherichia coli Nissle 1917-based therapeutics
Abstract
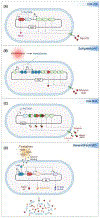
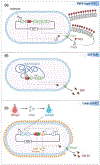
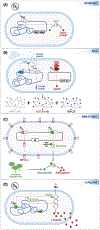
Engineered microbes are rapidly being developed for the delivery of therapeutic modalities to sites of disease. Escherichia coli Nissle 1917 (EcN), a genetically tractable probiotic with a well-established human safety record, is emerging as a favored chassis. Here, we summarize the latest progress in rationally engineered variants of EcN for the treatment of infectious diseases, metabolic disorders, and inflammatory bowel diseases (IBDs) when administered orally, as well as cancers when injected directly into tumors or the systemic circulation. We also discuss emerging studies that raise potential safety concerns regarding these EcN-based strains as therapeutics due to their secretion of a genotoxic colibactin that can promote the formation of DNA double-stranded breaks in mammalian DNA.
Keywords: Escherichia coli Nissle 1917; bioengineering; colibactin; microbial therapeutics; synthetic biology.
Copyright © 2022 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests C.F.L. is a member of the Scientific Advisory Board of Synlogic, Inc.
Figures
References
-
- Nißle A Weiteres über Grundlagen und Praxis der Mutaflorbehandlung. Dtsch Med Wochenschr 51, 1809–1813 (1925).
-
- Nissle A Die antagonistische behandlung chronischer darmstörungen mit colibakterien. Med Klin 2, 29–33 (1918).
-
- Sonnenborn U & Schulze J The non-pathogenic Escherichia coli strain Nissle 1917 – features of a versatile probiotic. Microbial Ecology in Health and Disease 21, 122–158 (2009).
-
- Kelly VW, Liang BK & Sirk SJ Living Therapeutics: The Next Frontier of Precision Medicine. ACS synthetic biology 9, 3184–3201 (2020). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

