Epidemiology of Cancers in Zambia: A significant variation in Cancer incidence and prevalence across the nation
- PMID: 35233276
- PMCID: PMC8843183
- DOI: 10.4314/mmj.v33i3.6
Epidemiology of Cancers in Zambia: A significant variation in Cancer incidence and prevalence across the nation
Abstract
Background: Cancer is one of the leading causes of death worldwide. More than two-thirds of deaths due to cancers occur in low- and middle-income countries where Zambia belongs. This study, therefore, sought to assess the epidemiology of various types of cancers in Zambia.
Methods: We conducted a retrospective observational study using the Zambia National Cancer Registry (ZNCR) population based data from 2007 to 2014. Zambia Central Statistics Office (CSO) demographic data were used to determine catchment area denominator used to calculate prevalence and incidence rates of cancers. Age-adjusted rates and case fatality rates were estimated using standard methods. We used a Poisson Approximation for calculating 95% confidence intervals (CI).
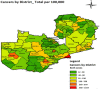
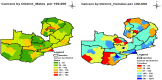
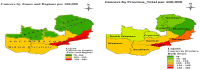
Results: The seven most cancer prevalent districts in Zambia were Luangwa, Kabwe, Lusaka, Monze, Mongu, Katete and Chipata. Cervical cancer, prostate cancer, breast cancer and Kaposi's sarcoma were the four most prevalent cancers as well as major causes of cancer related deaths in Zambia. Age adjusted rates and 95% CI for these cancers were: cervix uteri (186.3; CI = 181.77 - 190.83), prostate (60.03; CI = 57.03 - 63.03), breast (38.08; CI = 36.0 - 40.16) and Kaposi's sarcoma (26.18; CI = 25.14 - 27.22). CFR were: Leukaemia (38.1%); pancreatic cancer (36.3%); lung cancer (33.3%); and brain, nervous system (30.2%). The cancer population was associated with HIV with p-value of 0.000 and a Pearson correlation coefficient of 0.818.
Conclusions: The widespread distribution of cancers with high prevalence observed in the southern zone may have been perpetrated by lifestyle and sexual culture (traditional male circumcision known to prevent STIs is practiced in the northern belt) as well as geography. Intensifying cancer screening and early detection countrywide as well as changing the lifestyle and sexual culture would greatly help in the reduction of cancer cases in Zambia.
Keywords: Breast cancer; Cancer epidemiology; Cancers in Zambia; Cervical cancer; Kaposi's sarcoma; Prostate cancer.
© 2021 The College of Medicine and the Medical Association of Malawi.
Figures
References
-
- de Martel C, Georges D, Bray F, Ferlay J, Clifford GM. Global burden of cancer attributable to infections in 2018: a worldwide incidence analysis. Lancet Glob Health. 2020 Feb;8(2):e180–e190. - PubMed
-
- Fitzmaurice C, Allen C, Baber RM, et al. Global Burden of Disease Cancer Collaboration Global, regional, and national cancer incidence, mortality, years of life lost, years lived with disability, and disability-adjusted life-years for 32 cancer groups, 1990 to 2015: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study. JAMA Oncol. 2017;3(4):524–548. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ferlay J, Shin HR, Bray F, Forman D, Mathers C, Parkin DM. Estimates of worldwide burden of cancer in 2008: GLOBOCAN 2008. Int J Cancer. 2010;127:2893–2917. - PubMed
-
- James SL, Abate D, Abate KH, et al. GBD 2017 Disease and Injury Incidence and Prevalence Collaborators Global, regional, and national incidence, prevalence, and years lived with disability for 354 diseases and injuries for 195 countries and territories, 1990–2017: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Lancet. 2018;392(10159):1789–1858. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Global Burden of Disease Cancer Collaboration, author. Global, Regional, and National Cancer Incidence, Mortality, Years of Life Lost, Years Lived With Disability, and Disability-Adjusted Life-Years for 29 Cancer Groups, 1990 to 2017: A Systematic Analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study. JAMA Oncol. 2019;5(12):1749–1768. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical