A Case Series of Statin-Induced Necrotizing Autoimmune Myopathy
- PMID: 35233301
- PMCID: PMC8881230
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.21613
A Case Series of Statin-Induced Necrotizing Autoimmune Myopathy
Abstract
The use of statins has been increasing over the past decade for the primary and secondary prevention of cardiovascular disease worldwide. Subsequently, various side effects have also been unfolding. Muscle-related side effects secondary to statins range from myalgia to rhabdomyolysis and need close monitoring for early detection. Statin-induced necrotizing autoimmune myopathy (SINAM) in particular is unique given its pathophysiology, trigger factor, genetic predisposition, and aggressive management strategy. We present two cases of SINAM and discuss the clinical aspects of diagnosis, investigation, and management. Statin-induced necrotizing autoimmune myopathy usually presents with proximal myopathy along with increased creatinine kinase (CK) levels which do not resolve with only statin discontinuation. Diagnosis should be made with biopsy and 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-coenzyme A reductase (HMGCR) antibody detection. The investigation should also be directed to rule out other etiology of proximal myopathy. In most cases, rechallenge with a statin is unsuccessful and immunosuppressive treatment is essential.
Keywords: idiopathic rhabdomyolysis; proximal weakness; sinam; statin; statin-induced myopathy; statin-induced necrotizing autoimmune myopathy.
Copyright © 2022, Sharma et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures



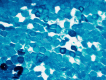

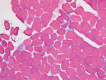

References
-
- Proximal myopathy: diagnostic approach and initial management. Suresh E, Wimalaratna S. Postgrad Med J. 2013;89:470–477. - PubMed
-
- Narrative review: statin-related myopathy. Joy TR, Hegele RA. Ann Intern Med. 2009;150:858–868. - PubMed
-
- Statin-associated autoimmune myopathy. Mammen AL. N Engl J Med. 2016;374:664–669. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
