Comparison of Solitaire and Neuroform Stenting for Coiling of Intracranial Bifurcation Aneurysms
- PMID: 35234080
- PMCID: PMC10152827
- DOI: 10.1177/15910199221081249
Comparison of Solitaire and Neuroform Stenting for Coiling of Intracranial Bifurcation Aneurysms
Abstract
Purpose: To compare the technical performance and outcomes of Solitaire and Neuroform stents for treatment of intracranial bifurcation aneurysms (IBAs).
Methods: IBAs treated by stent-assisted coiling using a Solitaire or Neuroform stent between October 2010 and December 2019 were retrospectively evaluated. Patient demographics, aneurysm information, treatment technique, periprocedural and device-related complications, parent artery angle change, along with initial and follow-up angiographic results were analyzed.
Results: One hundred twenty-one patients with 121 IBAs treated with Solitaire (n = 101) or Neuroform (n = 20) stent-assisted coiling were included. Aneurysm size, thrombotic and hemorrhagic complication rate, initial occlusion rate and in-stent stenosis between the two cohorts were not significantly different. Aneurysm location was significantly different between the two groups (p = 0.032). Jailing technique rate for coiling was significantly higher in the Solitaire than the Neuroform group (70.3% vs. 35.0%, p < 0.01). Follow-up DSA demonstrated a significantly lower recurrence rate for the Solitaire cohort (2.9% vs. 22.2%, p = 0.016). Parent artery angle changes, immediately post-operative and on follow-up were significantly greater in the Solitaire stent group (p < 0.05).
Conclusions: For intracranial bifurcation aneurysms, Solitaire stent-assisted coiling achieved a significantly lower recurrence rate and induced more favorable parent artery angular remodeling than Neuroform stenting.
Keywords: Neuroform; Solitaire; embolization; intracranial bifurcation aneurysm.
Conflict of interest statement
The author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures
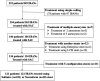

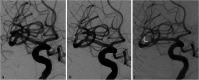
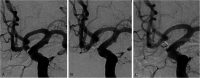
References
-
- Chalouhi N, Hoh BL, Hasan D. Review of cerebral aneurysm formation, growth, and rupture. Stroke 2013;44:3613–3622. - PubMed
-
- Can A, Ho AL, Dammers Ret al. et al. Morphological parameters associated with middle cerebral artery aneurysms. Neurosurgery 2015;76:721–726; discussion 726-727. - PubMed
-
- Zhang XJ, Gao BL, Hao WLet al. et al. Presence of anterior communicating artery aneurysm Is associated With Age, bifurcation angle, and vessel diameter. Stroke 2018;49:341–347. - PubMed
-
- Song J, Zhu F, Qian Y, et al. Morphological and hemodynamic differences between aneurysmal middle cerebral artery bifurcation and contralateral nonaneurysmal anatomy. Neurosurgery 2017;81:779–786. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

