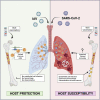
BCG vaccination provides protection against IAV but not SARS-CoV-2
- PMID: 35235831
- PMCID: PMC8858710
- DOI: 10.1016/j.celrep.2022.110502
BCG vaccination provides protection against IAV but not SARS-CoV-2
Abstract
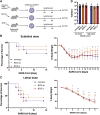
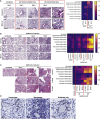
Since the vast majority of species solely rely on innate immunity for host defense, it stands to reason that a critical evolutionary trait like immunological memory evolved in this primitive branch of our immune system. There is ample evidence that vaccines such as bacillus Calmette-Guérin (BCG) induce protective innate immune memory responses (trained immunity) against heterologous pathogens. Here we show that while BCG vaccination significantly reduces morbidity and mortality against influenza A virus (IAV), it fails to provide protection against severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-2 (SARS-CoV-2). In contrast to IAV, SARS-CoV-2 infection leads to unique pulmonary vasculature damage facilitating viral dissemination to other organs, including the bone marrow (BM), a central site for BCG-mediated trained immunity. Finally, monocytes from BCG-vaccinated individuals mount an efficient cytokine response to IAV infection, while this response is minimal following SARS-CoV-2. Collectively, our data suggest that the protective capacity of BCG vaccination is contingent on viral pathogenesis and tissue tropism.
Keywords: BCG vaccination; SARS-CoV-2; animal models; hematopoietic stem cells; influenza virus; lung pathology; monocytes; trained immunity.
Copyright © 2022 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- Aaby P., Roth A., Ravn H., Napirna B.M., Rodrigues A., Lisse I.M., Stensballe L., Diness B.R., Lausch K.R., Lund N., et al. Randomized trial of BCG vaccination at birth to low-birth-weight children: beneficial nonspecific effects in the neonatal period? J. Infect Dis. 2011;204:245–252. - PubMed
-
- Arts R.J.W., Moorlag S., Novakovic B., Li Y., Wang S.Y., Oosting M., Kumar V., Xavier R.J., Wijmenga C., Joosten L.A.B., et al. BCG vaccination protects against experimental viral infection in humans through the induction of cytokines associated with trained immunity. Cell Host Microbe. 2018;23:89–100. e5. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

