Genes To Mental Health (G2MH): A Framework to Map the Combined Effects of Rare and Common Variants on Dimensions of Cognition and Psychopathology
- PMID: 35236119
- PMCID: PMC9345000
- DOI: 10.1176/appi.ajp.2021.21040432
Genes To Mental Health (G2MH): A Framework to Map the Combined Effects of Rare and Common Variants on Dimensions of Cognition and Psychopathology
Abstract
Rare genomic disorders (RGDs) confer elevated risk for neurodevelopmental psychiatric disorders. In this era of intense genomics discoveries, the landscape of RGDs is rapidly evolving. However, there has not been comparable progress to date in scalable, harmonized phenotyping methods. As a result, beyond associations with categorical diagnoses, the effects on dimensional traits remain unclear for many RGDs. The nature and specificity of RGD effects on cognitive and behavioral traits is an area of intense investigation: RGDs are frequently associated with more than one psychiatric condition, and those studied to date affect, to varying degrees, a broad range of developmental and cognitive functions. Although many RGDs have large effects, phenotypic expression is typically influenced by additional genomic and environmental factors. There is emerging evidence that using polygenic risk scores in individuals with RGDs offers opportunities to refine prediction, thus allowing for the identification of those at greatest risk of psychiatric illness. However, translation into the clinic is hindered by roadblocks, which include limited genetic testing in clinical psychiatry, and the lack of guidelines for following individuals with RGDs, who are at high risk of developing psychiatric symptoms. The Genes to Mental Health Network (G2MH) is a newly funded National Institute of Mental Health initiative that will collect, share, and analyze large-scale data sets combining genomics and dimensional measures of psychopathology spanning diverse populations and geography. The authors present here the most recent understanding of the effects of RGDs on dimensional behavioral traits and risk for psychiatric conditions and discuss strategies that will be pursued within the G2MH network, as well as how expected results can be translated into clinical practice to improve patient outcomes.
Keywords: Autism Spectrum Disorder; Diagnosis and Classification; Genetics/Genomics; Intellectual Disabilities; Neurodevelopmental Disorders; Schizophrenia Spectrum and Other Psychotic Disorders.
Figures
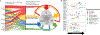
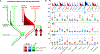

References
-
- Tammimies K, Marshall CR, Walker S, et al. : Molecular Diagnostic Yield of Chromosomal Microarray Analysis and Whole-Exome Sequencing in Children With Autism Spectrum Disorder. JAMA 2015; 314:895–903 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- R01 MH107431/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- U01 MH119736/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- U01 MH119738/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- P50 HD105351/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- 204824/Z/16/Z/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- U01 MH119689/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH085953/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- U01 MH119705/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- MRF-154-0001-RG-SKUSE/MRF_/MRF_/United Kingdom
- MR/N022572/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- P01 HD070454/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- MR/T033045/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MRF-058-0015-F-CHAW-C0867/MRF_/MRF_/United Kingdom
- U01 MH119741/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- U01 MH119690/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- MR/L011166/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- U01 MH119739/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- U01 MH119740/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM125757/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- U01 MH119737/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- U01 MH119746/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- MR/L010305/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- P50 HD103525/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- R37 MH085953/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH101221/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- U01 MH119759/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

