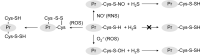Hydrogen Sulfide (H2S) Signaling as a Protective Mechanism against Endogenous and Exogenous Neurotoxicants
- PMID: 35236265
- PMCID: PMC9886801
- DOI: 10.2174/1570159X20666220302101854
Hydrogen Sulfide (H2S) Signaling as a Protective Mechanism against Endogenous and Exogenous Neurotoxicants
Abstract
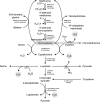
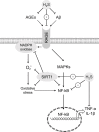
In view of the significant role of H2S in brain functioning, it is proposed that H2S may also possess protective effects against adverse effects of neurotoxicants. Therefore, the objective of the present review is to discuss the neuroprotective effects of H2S against toxicity of a wide spectrum of endogenous and exogenous agents involved in the pathogenesis of neurological diseases as etiological factors or key players in disease pathogenesis. Generally, the existing data demonstrate that H2S possesses neuroprotective effects upon exposure to endogenous (amyloid β, glucose, and advanced-glycation end-products, homocysteine, lipopolysaccharide, and ammonia) and exogenous (alcohol, formaldehyde, acrylonitrile, metals, 6-hydroxydopamine, as well as 1-methyl-4-phenyl- 1,2,3,6- tetrahydropyridine (MPTP) and its metabolite 1-methyl-4-phenyl pyridine ion (MPP)) neurotoxicants. On the one hand, neuroprotective effects are mediated by S-sulfhydration of key regulators of antioxidant (Sirt1, Nrf2) and inflammatory response (NF-κB), resulting in the modulation of the downstream signaling, such as SIRT1/TORC1/CREB/BDNF-TrkB, Nrf2/ARE/HO-1, or other pathways. On the other hand, H2S appears to possess a direct detoxicative effect by binding endogenous (ROS, AGEs, Aβ) and exogenous (MeHg) neurotoxicants, thus reducing their toxicity. Moreover, the alteration of H2S metabolism through the inhibition of H2S-synthetizing enzymes in the brain (CBS, 3-MST) may be considered a significant mechanism of neurotoxicity. Taken together, the existing data indicate that the modulation of cerebral H2S metabolism may be used as a neuroprotective strategy to counteract neurotoxicity of a wide spectrum of endogenous and exogenous neurotoxicants associated with neurodegeneration (Alzheimer's and Parkinson's disease), fetal alcohol syndrome, hepatic encephalopathy, environmental neurotoxicant exposure, etc. In this particular case, modulation of H2S-synthetizing enzymes or the use of H2S-releasing drugs should be considered as the potential tools, although the particular efficiency and safety of such interventions are to be addressed in further studies.
Keywords: Hydrogen sulfide; alcohol; amyloid; metals; neurotoxicants; sodium hydrosulfide.
Copyright© Bentham Science Publishers; For any queries, please email at epub@benthamscience.net.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Activation of autophagic flux and the Nrf2/ARE signaling pathway by hydrogen sulfide protects against acrylonitrile-induced neurotoxicity in primary rat astrocytes.Arch Toxicol. 2018 Jun;92(6):2093-2108. doi: 10.1007/s00204-018-2208-x. Epub 2018 May 3. Arch Toxicol. 2018. PMID: 29725710
-
The BDNF-TrkB signaling pathway is partially involved in the neuroprotective effects of hydrogen sulfide in Parkinson's disease.Eur J Pharmacol. 2023 Apr 5;944:175595. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2023.175595. Epub 2023 Feb 18. Eur J Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 36804547
-
Impaired CBS-H2S signaling axis contributes to MPTP-induced neurodegeneration in a mouse model of Parkinson's disease.Brain Behav Immun. 2018 Jan;67:77-90. doi: 10.1016/j.bbi.2017.07.159. Epub 2017 Aug 1. Brain Behav Immun. 2018. PMID: 28774789
-
Neuroprotective effects of hydrogen sulfide and the underlying signaling pathways.Rev Neurosci. 2015;26(2):129-42. doi: 10.1515/revneuro-2014-0051. Rev Neurosci. 2015. PMID: 25528761 Review.
-
Hydrogen sulfide and its donors for the treatment of traumatic brain injury: A comprehensive review.Int J Pharm. 2025 Jul 25;680:125792. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2025.125792. Epub 2025 May 28. Int J Pharm. 2025. PMID: 40446877 Review.
Cited by
-
Quantification of persulfidation on specific proteins: are we nearly there yet?Essays Biochem. 2024 Dec 4;68(4):467-478. doi: 10.1042/EBC20230095. Essays Biochem. 2024. PMID: 39290133 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hydrogen Sulfide (H2S- or H2Sn-Polysulfides) in Synaptic Plasticity: Modulation of NMDA Receptors and Neurotransmitter Release in Learning and Memory.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Mar 28;26(7):3131. doi: 10.3390/ijms26073131. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40243915 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Role of Hydrogen Sulfide (H2S) in Epigenetic Regulation of Neurodegenerative Diseases: A Systematic Review.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Aug 8;24(16):12555. doi: 10.3390/ijms241612555. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37628735 Free PMC article.
-
Protein Oxidative Modifications in Neurodegenerative Diseases: From Advances in Detection and Modelling to Their Use as Disease Biomarkers.Antioxidants (Basel). 2024 May 31;13(6):681. doi: 10.3390/antiox13060681. Antioxidants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38929122 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hydrogen Sulfide Attenuates Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Inflammation via the P-glycoprotein and NF-κB Pathway in Astrocytes.Neurochem Res. 2023 May;48(5):1424-1437. doi: 10.1007/s11064-022-03840-5. Epub 2022 Dec 8. Neurochem Res. 2023. PMID: 36482035 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources