The long and short non-coding RNAs modulating EZH2 signaling in cancer
- PMID: 35236381
- PMCID: PMC8892735
- DOI: 10.1186/s13045-022-01235-1
The long and short non-coding RNAs modulating EZH2 signaling in cancer
Erratum in
-
Correction: The long and short non-coding RNAs modulating EZH2 signaling in cancer.J Hematol Oncol. 2022 May 6;15(1):50. doi: 10.1186/s13045-022-01276-6. J Hematol Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35524266 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
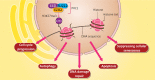
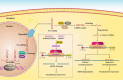
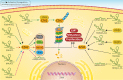
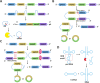
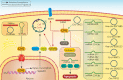
Non-coding RNAs (ncRNAs) are a large family of RNA molecules with no capability in encoding proteins. However, they participate in developmental and biological processes and their abnormal expression affects cancer progression. These RNA molecules can function as upstream mediators of different signaling pathways and enhancer of zeste homolog 2 (EZH2) is among them. Briefly, EZH2 belongs to PRCs family and can exert functional roles in cells due to its methyltransferase activity. EZH2 affects gene expression via inducing H3K27me3. In the present review, our aim is to provide a mechanistic discussion of ncRNAs role in regulating EZH2 expression in different cancers. MiRNAs can dually induce/inhibit EZH2 in cancer cells to affect downstream targets such as Wnt, STAT3 and EMT. Furthermore, miRNAs can regulate therapy response of cancer cells via affecting EZH2 signaling. It is noteworthy that EZH2 can reduce miRNA expression by binding to promoter and exerting its methyltransferase activity. Small-interfering RNA (siRNA) and short-hairpin RNA (shRNA) are synthetic, short ncRNAs capable of reducing EZH2 expression and suppressing cancer progression. LncRNAs mainly regulate EZH2 expression via targeting miRNAs. Furthermore, lncRNAs induce EZH2 by modulating miRNA expression. Circular RNAs (CircRNAs), like lncRNAs, affect EZH2 expression via targeting miRNAs. These areas are discussed in the present review with a focus on molecular pathways leading to clinical translation.
Keywords: Cancer therapy; CircRNA; EZH2; LncRNA; MiRNA; ShRNA; SiRNA.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Abadi AJ, Zarrabi A, Hashemi F, Zabolian A, Najafi M, Entezari M, Hushmandi K, Aref AR, Khan H, Makvandi P, et al. The role of SOX family transcription factors in gastric cancer. Int J Biol Macromol. 2021;180:608–624. - PubMed
-
- Ashrafizadeh M, Delfi M, Hashemi F, Zabolian A, Saleki H, Bagherian M, Azami N, Farahani MV, Sharifzadeh SO, Hamzehlou S, et al. Biomedical application of chitosan-based nanoscale delivery systems: Potential usefulness in siRNA delivery for cancer therapy. Carbohydr Polym. 2021;260:117809. - PubMed
-
- Mohan CD, Bharathkumar H, Dukanya, Rangappa S, Shanmugam MK, Chinnathambi A, Alharbi SA, Alahmadi TA, Bhattacharjee A, Lobie PE, et al. N-substituted pyrido-1,4-oxazin-3-ones induce apoptosis of hepatocellular carcinoma cells by targeting NF-κB signaling pathway. Front Pharmacol. 2018;9:1125. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Cai W, Xiong Chen Z, Rane G, Satendra Singh S, Choo Z, Wang C, Yuan Y, Zea Tan T, Arfuso F, Yap CT, et al. Wanted DEAD/H or alive: helicases winding up in cancers. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2017;109. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

