Neuromorphic Engineering Needs Closed-Loop Benchmarks
- PMID: 35237122
- PMCID: PMC8884247
- DOI: 10.3389/fnins.2022.813555
Neuromorphic Engineering Needs Closed-Loop Benchmarks
Abstract
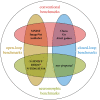
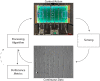
Neuromorphic engineering aims to build (autonomous) systems by mimicking biological systems. It is motivated by the observation that biological organisms-from algae to primates-excel in sensing their environment, reacting promptly to their perils and opportunities. Furthermore, they do so more resiliently than our most advanced machines, at a fraction of the power consumption. It follows that the performance of neuromorphic systems should be evaluated in terms of real-time operation, power consumption, and resiliency to real-world perturbations and noise using task-relevant evaluation metrics. Yet, following in the footsteps of conventional machine learning, most neuromorphic benchmarks rely on recorded datasets that foster sensing accuracy as the primary measure for performance. Sensing accuracy is but an arbitrary proxy for the actual system's goal-taking a good decision in a timely manner. Moreover, static datasets hinder our ability to study and compare closed-loop sensing and control strategies that are central to survival for biological organisms. This article makes the case for a renewed focus on closed-loop benchmarks involving real-world tasks. Such benchmarks will be crucial in developing and progressing neuromorphic Intelligence. The shift towards dynamic real-world benchmarking tasks should usher in richer, more resilient, and robust artificially intelligent systems in the future.
Keywords: ATIS; DAVIS; DVS; audio; benchmarks; event-based systems; neuromorphic engineering; olfaction.
Copyright © 2022 Milde, Afshar, Xu, Marcireau, Joubert, Ramesh, Bethi, Ralph, El Arja, Dennler, van Schaik and Cohen.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Åström K. J., Bernhardsson B. M.. (2002). Comparison of Riemann and Lebesgue sampling for first order stochastic systems, in Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Decision and Control, Vol. 2 (Las Vegas, NV: IEEE; ), 2011–2016.
-
- Åström K. J., Murray R. M. (2010). Feedback Systems: An Introduction for Scientists and Engineers. Princeton, NJ: Princeton University Press.
-
- Abu-El-Haija S., Kothari N., Lee J., Natsev P., Toderici G., Varadarajan B., et al. . (2016). YouTube-8M: a large-scale video classification benchmark. arXiv preprint arXiv:1609.08675.
-
- Aimar A., Mostafa H., Calabrese E., Rios-Navarro A., Tapiador-Morales R., Lungu I. A., et al. . (2019). NullHop: a flexible convolutional neural network accelerator based on sparse representations of feature maps. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 30, 644–656. 10.1109/TNNLS.2018.2852335 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Akimov D. (2020). Distributed soft actor-critic with multivariate reward representation and knowledge distillation. arXiv preprint arXiv:1911.13056.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

