Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor Mechanisms Affecting Chronic Kidney Disease
- PMID: 35237156
- PMCID: PMC8882872
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2022.782199
Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor Mechanisms Affecting Chronic Kidney Disease
Abstract
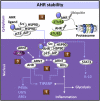
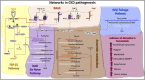
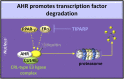
The aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AHR) is a basic helix-loop-helix transcription factor that binds diverse endogenous and xenobiotic ligands, which regulate AHR stability, transcriptional activity, and cell signaling. AHR activity is strongly implicated throughout the course of chronic kidney disease (CKD). Many diverse organic molecules bind and activate AHR and these ligands are reported to either promote glomerular and tubular damage or protect against kidney injury. AHR crosstalk with estrogen, peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-γ, and NF-κB pathways may contribute to the diversity of AHR responses during the various forms and stages of CKD. The roles of AHR in kidney fibrosis, metabolism and the renin angiotensin system are described to offer insight into CKD pathogenesis and therapies.
Keywords: PPAR γ; RAAS; TGF—β1; aryl hydrocarbon (Ah) receptor; hypoxia; kynurenine.
Copyright © 2022 Curran and Kopp.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Addi T., Poitevin S., McKay N., El Mecherfi K. E., Kheroua O., Jourde-Chiche N., et al. (2019). Mechanisms of Tissue Factor Induction by the Uremic Toxin Indole-3 Acetic Acid through Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor/nuclear Factor-Kappa B Signaling Pathway in Human Endothelial Cells. Arch. Toxicol. 93 (1), 121–136. 10.1007/s00204-018-2328-3 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Asai H., Hirata J., Watanabe-Akanuma M. (2018). Indoxyl Glucuronide, a Protein-Bound Uremic Toxin, Inhibits Hypoxia-Inducible Factor‒dependent Erythropoietin Expression through Activation of Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 504 (2), 538–544. 10.1016/j.bbrc.2018.09.018 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Assefa E. G., Yan Q., Gezahegn S. B., Salissou M. T. M., He S., Wu N., et al. (20192019). Role of Resveratrol on Indoxyl Sulfate-Induced Endothelial Hyperpermeability via Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor (AHR)/Src-Dependent Pathway. Oxid Med. Cel Longev 2019, 5847040. 10.1155/2019/5847040 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

