Erythrocyte Indices in Creutzfeldt-Jakob Disease Predict Survival Time
- PMID: 35237232
- PMCID: PMC8884143
- DOI: 10.3389/fneur.2022.839081
Erythrocyte Indices in Creutzfeldt-Jakob Disease Predict Survival Time
Abstract
Background: Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease (CJD) is a devastating neurodegenerative disease caused by propagation of abnormally folded prion proteins (PrPSc). Some fluid biomarkers have been reported to be associated with disease duration in CJD. Based on studies which have found that prion protein (PrPC) played a role in erythrocytic hematopoiesis, we evaluated the association between peripheral red blood cell indices and survival time in CJD.
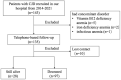
Methods: We retrospectively collected data on peripheral red blood cell indices, including red blood cell (RBC) count, hemoglobin (Hb), hematocrit (HCT), mean corpuscular volume (MCV), mean corpuscular hemoglobin (MCH), mean corpuscular hemoglobin concentration (MCHC), and red cell distribution width (RDW), from 125 CJD patients. Cox proportional hazard models were generated to determine whether red cell indices correlated with survival time of patients with CJD.
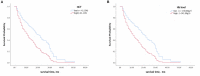
Results: Of the 125 included participants, 70 (56%) were male, and the mean age at diagnosis (SD) was 60.3 (9.5) years. Hemoglobin levels (hazard ratio 1.710, 95% CI 1.124-2.600, p = 0.012) and HCT (hazard ratio 1.689, 95% CI 1.112-2.565, p=0.014) were significantly associated with survival time after controlling for sex, age, and Barthel Index. Red blood cell count, MCV, MCH, MCHC, and RDW were not associated with survival time before or after adjusting for covariates.
Conclusions: Our study found that Hb and HCT were significantly associated with survival time in patients with CJD. These results may inform evaluation of the mechanisms of interaction between prion disease and hematopoiesis, and indicate that Hb and HCT may be potential prognostic biomarkers.
Keywords: Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease; erythrocyte indices; hematocrit; hemoglobin; red cell indices; survival time.
Copyright © 2022 Kong, Chen, Zhang and Wu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

