Bacteriophage Lytic Enzyme P9ly as an Alternative Antibacterial Agent Against Antibiotic-Resistant Shigella dysenteriae and Staphylococcus aureus
- PMID: 35237249
- PMCID: PMC8882861
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.821989
Bacteriophage Lytic Enzyme P9ly as an Alternative Antibacterial Agent Against Antibiotic-Resistant Shigella dysenteriae and Staphylococcus aureus
Abstract
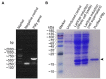
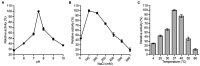
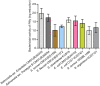
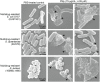
Developing new strategies to replace or supplement antibiotics to combat bacterial infection is a pressing task in the field of microbiological research. In this study, we report a lytic enzyme named P9ly deriving from the bacteriophage PSD9 that could infect multidrug-resistant Shigella. This enzyme was identified through whole-genome sequencing of PSD9. The results show that P9ly contains a conserved T4-like_lys domain and belongs to the phage lysozyme family. Recombinant P9ly obtained from protein purification presented biological activity and could digest bacterial cell walls (CW), resulting in the destruction of cell structure and leakage of intracellular components. Furthermore, P9ly exhibited bacteriolytic and bactericidal activity on different strains, especially multidrug-resistant Gram-negative Shigella dysenteriae and Gram-positive Staphylococcus aureus. Additionally, combined use of P9ly with ceftriaxone sodium (CRO) could decrease necessary dose of the antibiotic used and improve the antibacterial effect. In summary, under the current backdrop of extensive antibiotic usage and the continuous emergence of bacterial resistance, this study provides an insight into developing bacteriophage-based antibacterial agents against both Gram-negative and Gram-positive pathogens.
Keywords: antibiotic resistance; bacteriolytic activity; bacteriophage; bioengineering; endolysin.
Copyright © 2022 Wang, Xiao, Lu, Deng, Deng and Lin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures




References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

