Prognostication of Pancreatic Cancer Using The Cancer Genome Atlas Based Ferroptosis-Related Long Non-Coding RNAs
- PMID: 35237306
- PMCID: PMC8883032
- DOI: 10.3389/fgene.2022.838021
Prognostication of Pancreatic Cancer Using The Cancer Genome Atlas Based Ferroptosis-Related Long Non-Coding RNAs
Abstract
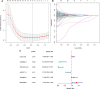
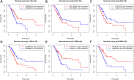
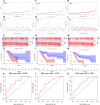
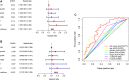
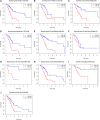
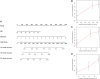
Background: Long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) are key regulators of pancreatic cancer development and are involved in ferroptosis regulation. LncRNA transcript levels serve as a prognostic factor for pancreatic cancer. Therefore, identifying ferroptosis-related lncRNAs (FRLs) with prognostic value in pancreatic cancer is critical. Methods: In this study, FRLs were identified by combining The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) and FerrDb databases. For training cohort, univariate Cox, Lasso, and multivariate Cox regression analyses were applied to identify prognosis FRLs and then construct a prognostic FRLs signature. Testing cohort and entire cohort were applied to validate the prognostic signature. Moreover, the nomogram was performed to predict prognosis at different clinicopathological stages and risk scores. A co-expression network with 76 lncRNA-mRNA targets was constructed. Results: Univariate Cox analysis was performed to analyze the prognostic value of 193 lncRNAs. Furthermore, the least absolute shrinkage and selection operator and the multivariate Cox analysis were used to assess the prognostic value of these ferroptosis-related lncRNAs. A prognostic risk model, of six lncRNAs, including LINC01705, AC068620.2, TRAF3IP2-AS1, AC092171.2, AC099850.3, and MIR193BHG was constructed. The Kaplan Meier (KM) and time-related receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve analysis were performed to calculate overall survival and compare high- and low-risk groups. There was also a significant difference in survival time between the high-risk and low-risk groups for the testing cohort and the entire cohort, with AUCs of .723, .753, respectively. Combined with clinicopathological characteristics, the risk model was validated as a new independent prognostic factor for pancreatic adenocarcinoma through univariate and multivariate Cox regression. Moreover, a nomogram showed good prediction. Conclusion: The signature of six FRLs had significant prognostic value for pancreatic adenocarcinoma. They may be a promising therapeutic target in clinical practice.
Keywords: ferroptosis; long non-coding RNA; nomogram; pancreatic adenocarcinoma; risk model.
Copyright © 2022 Li, Zhang, Tao, Hong, Zhang and Chen.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Development and Validation of a Novel Ferroptosis-Related LncRNA Signature for Predicting Prognosis and the Immune Landscape Features in Uveal Melanoma.Front Immunol. 2022 Jun 14;13:922315. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.922315. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35774794 Free PMC article.
-
Development and validation of a novel ferroptosis‑related lncRNA prognostic signature for pancreatic adenocarcinoma.Mol Med Rep. 2023 Feb;27(2):56. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2023.12943. Epub 2023 Jan 20. Mol Med Rep. 2023. PMID: 36660936 Free PMC article.
-
Construction of a ferroptosis-related five-lncRNA signature for predicting prognosis and immune response in thyroid carcinoma.Cancer Cell Int. 2022 Sep 29;22(1):296. doi: 10.1186/s12935-022-02674-z. Cancer Cell Int. 2022. PMID: 36175889 Free PMC article.
-
Ferroptosis-related long non-coding RNA signature predicts the prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma: A Review.Medicine (Baltimore). 2022 Nov 25;101(47):e31747. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000031747. Medicine (Baltimore). 2022. PMID: 36451456 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identification of a competing endogenous RNA network associated with prognosis of pancreatic adenocarcinoma.Cancer Cell Int. 2020 Jun 11;20:231. doi: 10.1186/s12935-020-01243-6. eCollection 2020. Cancer Cell Int. 2020. PMID: 32536819 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A Noval Established Cuproptosis-Associated LncRNA Signature for Prognosis Prediction in Primary Hepatic Carcinoma.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2022 Sep 15;2022:2075638. doi: 10.1155/2022/2075638. eCollection 2022. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2022. PMID: 36159561 Free PMC article.
-
Downregulation of LINC01426 inhibits the proliferation and migration of human pancreatic cancer cells in vivo and in vitro.J Gastrointest Oncol. 2022 Dec;13(6):3278-3289. doi: 10.21037/jgo-22-1167. J Gastrointest Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36636053 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptome analysis identification of A-to-I RNA editing in granulosa cells associated with PCOS.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023 Jul 21;14:1170957. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1170957. eCollection 2023. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 37547318 Free PMC article.
-
Disulfidptosis classification of pancreatic carcinoma reveals correlation with clinical prognosis and immune profile.Hereditas. 2025 Feb 22;162(1):26. doi: 10.1186/s41065-025-00381-z. Hereditas. 2025. PMID: 39987145 Free PMC article.
-
Ferroptosis in pancreatic diseases: potential opportunities and challenges that require attention.Hum Cell. 2023 Jul;36(4):1233-1243. doi: 10.1007/s13577-023-00894-7. Epub 2023 Mar 16. Hum Cell. 2023. PMID: 36929283 Review.
References
-
- Du C., Zhang J.-l., Wang Y., Zhang Y.-y., Zhang J.-h., Zhang L.-f., et al. (2020). The Long Non-coding RNA LINC01705 Regulates the Development of Breast Cancer by Sponging miR-186-5p to Mediate TPR Expression as a Competitive Endogenous RNA. Front. Genet. 11, 779. 10.3389/fgene.2020.00779 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

