Impact of C-reactive protein and albumin levels on short, medium, and long term mortality in patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma
- PMID: 35238275
- PMCID: PMC8896183
- DOI: 10.1080/07853890.2022.2046287
Impact of C-reactive protein and albumin levels on short, medium, and long term mortality in patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma
Abstract
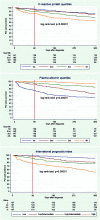
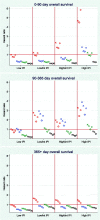
Objectives and study design: In this population-based study of 602 patients, we amended C-reactive protein (CRP) and plasma albumin (PA) levels around the diagnosis of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) to the International Prognostic Index (IPI) and assessed 0-90, 91-365, and +365-day survival.Results: The CRP did not contribute to the IPI's prognostic or discriminatory ability, regardless of time period, particularly not in models with PA. In contrast, the PA was an important contributor, especially in the 0-90 day period, but also up to one year after the diagnosis. For day 0-90, the model with the IPI only had an Area Under the Receiver Operating Characteristics (AUROC) of 0.742, whereas the IPI with PA as a continuous variable rendered an AUROC of 0.841. Especially the lower PA quartile (18-32 g/L) contributed to the worse prognosis.Conclusions: The amendment of PA to the IPI may significantly improve the short-term prognostic and discriminative ability.Key messagesThe amendment of the plasma albumin (PA) level to the International Prognostic Index significantly improved the prediction of mortality up to one year after the diagnosis of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma.It was especially the lower quartile of the PA level (18-32 g/L) that contributed to the worse prognosis.
Keywords: C-reactive protein; Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma; inflammation; plasma albumin; prognosis.
Conflict of interest statement
TSL: Bristol Myers Squibb/Celgene, Novartis, Roche, Gilead, Takeda – consultancy/advisory boards.
HF received support outside this work from Alexion, Gilead, Abbvie, Janssen Pharmaceuticals, and Novartis.
FGZ received grants for investigator initiated clinical trials from Bactiguard, Sweden, and Ionis Pharmaceuticals, USA.
RBD reports personal fees from Roche Diagnostics, outside the submitted work.
KOG, PJV, MI, PP, SLN, JKM, TGJ, MC, JEC, JJ report no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Utility of a simple prognostic stratification based on platelet counts and serum albumin levels in elderly patients with diffuse large B cell lymphoma.Ann Hematol. 2017 Jan;96(1):1-8. doi: 10.1007/s00277-016-2819-3. Epub 2016 Sep 19. Ann Hematol. 2017. PMID: 27641425
-
C-reactive protein level is a prognostic indicator for survival and improves the predictive ability of the R-IPI score in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma patients.Br J Cancer. 2014 Jul 8;111(1):55-60. doi: 10.1038/bjc.2014.277. Epub 2014 May 29. Br J Cancer. 2014. PMID: 24874478 Free PMC article.
-
Serum C-reactive protein as an important prognostic variable in patients with diffuse large B cell lymphoma.Tumour Biol. 2012 Aug;33(4):1039-44. doi: 10.1007/s13277-012-0337-z. Epub 2012 Feb 11. Tumour Biol. 2012. PMID: 22328138
-
Available prognostic models for risk stratification of diffuse large B cell lymphoma patients: a systematic review.Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2019 Jan;133:1-16. doi: 10.1016/j.critrevonc.2018.10.006. Epub 2018 Nov 1. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2019. PMID: 30661646
-
Interpretations of the Role of Plasma Albumin in Prognostic Indices: A Literature Review.J Clin Med. 2023 Sep 22;12(19):6132. doi: 10.3390/jcm12196132. J Clin Med. 2023. PMID: 37834777 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Derangements of immunological proteins in HIV-associated diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: the frequency and prognostic impact.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2024 Apr 3;14:1340096. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2024.1340096. eCollection 2024. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 38633747 Free PMC article.
-
A Novel and Validated Inflammation-Based Prognosis Score (IBPS) Predicts Outcomes in Patients with Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma.Cancer Manag Res. 2023 Jul 13;15:651-666. doi: 10.2147/CMAR.S408100. eCollection 2023. Cancer Manag Res. 2023. PMID: 37465083 Free PMC article.
-
Association between serum albumin levels and survival in elderly patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: a single-center retrospective study.Transl Cancer Res. 2023 Jun 30;12(6):1577-1587. doi: 10.21037/tcr-23-503. Transl Cancer Res. 2023. PMID: 37434675 Free PMC article.
-
Association of inflammatory risk based on the Glasgow Prognostic Score with long-term mortality in patients with cardiovascular disease.Sci Rep. 2025 Feb 22;15(1):6474. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-90238-2. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 39987233 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic value of lactate dehydrogenase to absolute lymphocyte count ratio and albumin to fibrinogen ratio in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma.Medicine (Baltimore). 2024 Jul 26;103(30):e39097. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000039097. Medicine (Baltimore). 2024. PMID: 39058821 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Oken MM, Creech RH, Tormey DC, et al. . Toxicity and response criteria of the Eastern cooperative oncology group. Am J Clin Oncol. 1982; 5(6):649–655. - PubMed
-
- International Non-Hodgkin's Lymphoma Prognostic Factors P. A predictive model for aggressive non-Hodgkin's lymphoma. NEJM. 1993; 329(14):987–994. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
