Loss-of-function variants in TIAM1 are associated with developmental delay, intellectual disability, and seizures
- PMID: 35240055
- PMCID: PMC9069076
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2022.01.020
Loss-of-function variants in TIAM1 are associated with developmental delay, intellectual disability, and seizures
Abstract
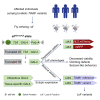
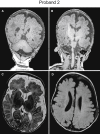
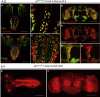
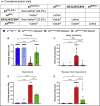
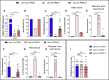
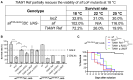
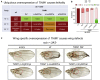
TIAM Rac1-associated GEF 1 (TIAM1) regulates RAC1 signaling pathways that affect the control of neuronal morphogenesis and neurite outgrowth by modulating the actin cytoskeletal network. To date, TIAM1 has not been associated with a Mendelian disorder. Here, we describe five individuals with bi-allelic TIAM1 missense variants who have developmental delay, intellectual disability, speech delay, and seizures. Bioinformatic analyses demonstrate that these variants are rare and likely pathogenic. We found that the Drosophila ortholog of TIAM1, still life (sif), is expressed in larval and adult central nervous system (CNS) and is mainly expressed in a subset of neurons, but not in glia. Loss of sif reduces the survival rate, and the surviving adults exhibit climbing defects, are prone to severe seizures, and have a short lifespan. The TIAM1 reference (Ref) cDNA partially rescues the sif loss-of-function (LoF) phenotypes. We also assessed the function associated with three TIAM1 variants carried by two of the probands and compared them to the TIAM1 Ref cDNA function in vivo. TIAM1 p.Arg23Cys has reduced rescue ability when compared to TIAM1 Ref, suggesting that it is a partial LoF variant. In ectopic expression studies, both wild-type sif and TIAM1 Ref are toxic, whereas the three variants (p.Leu862Phe, p.Arg23Cys, and p.Gly328Val) show reduced toxicity, suggesting that they are partial LoF variants. In summary, we provide evidence that sif is important for appropriate neural function and that TIAM1 variants observed in the probands are disruptive, thus implicating loss of TIAM1 in neurological phenotypes in humans.
Keywords: Drosophila; Sif; TIAM1; developmental delay; intellectual disability; seizures; speech delay; still life.
Copyright © 2022 American Society of Human Genetics. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests M.J.G.S. is a salaried employee of GeneDx Inc.
Figures

References
-
- Splinter K., Adams D.R., Bacino C.A., Bellen H.J., Bernstein J.A., Cheatle-Jarvela A.M., Eng C.M., Esteves C., Gahl W.A., Hamid R., et al. Undiagnosed Diseases Network Effect of Genetic Diagnosis on Patients with Previously Undiagnosed Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018;379:2131–2139. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1714458. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Wangler M.F., Yamamoto S., Chao H.T., Posey J.E., Westerfield M., Postlethwait J., Hieter P., Boycott K.M., Campeau P.M., Bellen H.J., Members of the Undiagnosed Diseases Network (UDN) Model Organisms Facilitate Rare Disease Diagnosis and Therapeutic Research. Genetics. 2017;207:9–27. doi: 10.1534/genetics.117.203067. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Coventry A., Bull-Otterson L.M., Liu X., Clark A.G., Maxwell T.J., Crosby J., Hixson J.E., Rea T.J., Muzny D.M., Lewis L.R., et al. Deep resequencing reveals excess rare recent variants consistent with explosive population growth. Nat. Commun. 2010;1:131. doi: 10.1038/ncomms1130. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

