Anti-inflammatory and anti-viral actions of anionic pulmonary surfactant phospholipids
- PMID: 35240310
- PMCID: PMC9050941
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbalip.2022.159139
Anti-inflammatory and anti-viral actions of anionic pulmonary surfactant phospholipids
Abstract
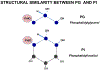
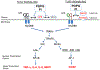
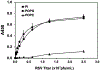
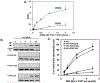
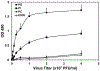
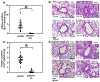
Pulmonary surfactant is a mixture of lipids and proteins, consisting of 90% phospholipid, and 10% protein by weight, found predominantly in pulmonary alveoli of vertebrate lungs. Two minor components of pulmonary surfactant phospholipids, phosphatidylglycerol (PG) and phosphatidylinositol (PI), are present within the alveoli at very high concentrations, and exert anti-inflammatory effects by regulating multiple Toll like receptors (TLR2/1, TLR4, and TLR2/6) by antagonizing cognate ligand-dependent activation. POPG also attenuates LPS-induced lung injury in vivo. In addition, these lipids bind directly to RSV and influenza A viruses (IAVs) and block interaction between host cells and virions, and thereby prevent viral replication in vitro. POPG and PI also inhibit RSV and IAV infection in vivo, in mice and ferrets. The lipids markedly inhibit SARS-CoV-2 infection in vitro. These findings suggest that both POPG and PI have strong potential to be applied as both prophylaxis and post-infection treatments for problematic respiratory viral infections.
Keywords: Antiviral; Innate immunity; Pulmonary surfactant phospholipids; Respiratory viruses; Toll-like receptors (TLRs).
Copyright © 2022 The Authors. Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interest
The authors declare the following financial interests/personal relationships which may be considered as potential competing interests: Mari Numata has patent Surfactant Lipids, Composition Thereof and Uses Thereof. issued to National Jewish Health. Dennis. R. Voelker has patent Surfactant Lipids, Composition Thereof and Uses Thereof. issued to National Jewish Health.
Figures
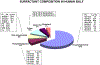


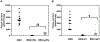
References
-
- Kuronuma K, Mitsuzawa H, Takeda K, Nishitani C, Chan ED, Kuroki Y, Nakamura M, Voelker DR, Anionic pulmonary surfactant phospholipids inhibit inflammatory responses from alveolar macrophages and U937 cells by binding the lipopolysaccharide-interacting proteins CD14 and MD-2, J. Biol. Chem 284 (38) (2009) 25488–25500, 10.1074/jbc.M109.040832, quiz 880-861. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Schmidt R, Meier U, Markart P, Grimminger F, Velcovsky HG, Morr H, Seeger W, Gunther A, Altered fatty acid composition of lung surfactant phospholipids in interstitial lung disease, Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell Mol. Physiol 283 (5) (2002) L1079–L1085, 10.1152/ajplung.00484.2001. Epub 2002/10/12. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

