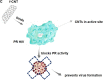
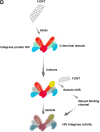
Coronavirus and Carbon Nanotubes: Seeking Immunological Relationships to Discover Immunotherapeutic Possibilities
- PMID: 35241912
- PMCID: PMC8887185
- DOI: 10.2147/IJN.S341890
Coronavirus and Carbon Nanotubes: Seeking Immunological Relationships to Discover Immunotherapeutic Possibilities
Abstract
Since December 2019, the world has faced an unprecedented pandemic crisis due to a new coronavirus disease, coronavirus disease-2019 (COVID-19), which has instigated intensive studies on prevention and treatment possibilities. Here, we investigate the relationships between the immune activation induced by three coronaviruses associated with recent outbreaks, with special attention to SARS-CoV-2, the causative agent of COVID-19, and the immune activation induced by carbon nanotubes (CNTs) to understand the points of convergence in immune induction and modulation. Evidence suggests that CNTs are among the most promising materials for use as immunotherapeutic agents. Therefore, this investigation explores new possibilities of effective immunotherapies for COVID-19. This study aimed to raise interest and knowledge about the use of CNTs as immunotherapeutic agents in coronavirus treatment. Thus, we summarize the most important immunological aspects of various coronavirus infections and describe key advances and challenges in using CNTs as immunotherapeutic agents against viral infections and the activation of the immune response induced by CNTs, which can shed light on the immunotherapeutic possibilities of CNTs.
Keywords: carbon nanotubes; coronavirus; immunomodulation; immunotherapy.
© 2022 de Carvalho Lima et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no declarations or conflicts of interest associated with this work.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Prevention and treatment of COVID-19 disease by controlled modulation of innate immunity.Eur J Immunol. 2020 Jul;50(7):932-938. doi: 10.1002/eji.202048693. Epub 2020 Jun 15. Eur J Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32438473 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Current status of antivirals and druggable targets of SARS CoV-2 and other human pathogenic coronaviruses.Drug Resist Updat. 2020 Dec;53:100721. doi: 10.1016/j.drup.2020.100721. Epub 2020 Aug 26. Drug Resist Updat. 2020. PMID: 33132205 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Systemic innate and adaptive immune responses to SARS-CoV-2 as it relates to other coronaviruses.Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2020 Dec 1;16(12):2980-2991. doi: 10.1080/21645515.2020.1802974. Epub 2020 Sep 2. Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2020. PMID: 32878546 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Treatment and prevention strategies for the COVID 19 pandemic: A review of immunotherapeutic approaches for neutralizing SARS-CoV-2.Int J Biol Macromol. 2021 Sep 1;186:490-500. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2021.07.013. Epub 2021 Jul 5. Int J Biol Macromol. 2021. PMID: 34237371 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The importance of vitamin d metabolism as a potential prophylactic, immunoregulatory and neuroprotective treatment for COVID-19.J Transl Med. 2020 Aug 26;18(1):322. doi: 10.1186/s12967-020-02488-5. J Transl Med. 2020. PMID: 32847594 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Antiviral nanomedicine: Advantages, mechanisms and advanced therapies.Bioact Mater. 2025 Jun 5;52:92-122. doi: 10.1016/j.bioactmat.2025.05.030. eCollection 2025 Oct. Bioact Mater. 2025. PMID: 40530413 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effects of Carbon Nanomaterials and Aloe vera on Melanomas-Where Are We? Recent Updates.Pharmaceutics. 2022 Sep 22;14(10):2004. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics14102004. Pharmaceutics. 2022. PMID: 36297440 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Modeling and Molecular Dynamics Studies of Flavone-DENV E-3 Protein-SWCNT Interaction at the Flavonoid Binding Sites.Viruses. 2025 Apr 4;17(4):525. doi: 10.3390/v17040525. Viruses. 2025. PMID: 40284968 Free PMC article.
-
Carbon-based nanomaterials against SARS-CoV-2: Therapeutic and diagnostic applications.OpenNano. 2023 Mar;10:100121. doi: 10.1016/j.onano.2023.100121. Epub 2023 Feb 18. OpenNano. 2023. PMID: 40478147 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous