Reduction of Hepatic Steatosis, Oxidative Stress, Inflammation, Ballooning and Insulin Resistance After Therapy with Safranal in NAFLD Animal Model: A New Approach
- PMID: 35241921
- PMCID: PMC8886028
- DOI: 10.2147/JIR.S354878
Reduction of Hepatic Steatosis, Oxidative Stress, Inflammation, Ballooning and Insulin Resistance After Therapy with Safranal in NAFLD Animal Model: A New Approach
Abstract
Introduction: Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is intimately linked to hepatic steatosis, inflammation, insulin resistance (IR), oxidative stress (OS), and ballooning. A high fat diet (HFD) is considered a major etiological factor that primarily covers the numerous features of NAFLD.
Methods: The present study aimed to evaluate the protective effect of safranal on hepatic steatosis, OS, liver index, IR index, liver function enzymes, plasma lipids, TNF-α, malondialdehyde (MDA), advanced oxidation protein products (AOPPs) and nitrite (NO2 -) levels in a NAFLD rat model fed with a HFD for 12 weeks. The ELISA kits were used to measure TNF-α and insulin in serum and plasma, respectively.
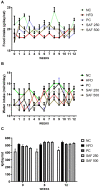
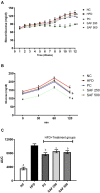
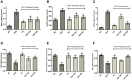
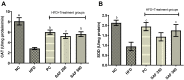
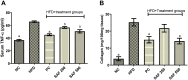
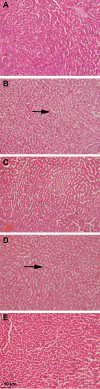
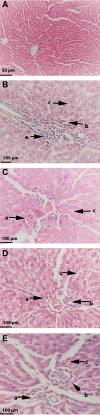
Results: HFD significantly induced hepatic steatosis, OS, IR, liver, and oxidative enzyme elevation and inflammation in experimental animals. Rats treated with safranal in ascending order of doses 250 and 500 mg/kg orally for 4-weeks showed a reduction in hepatic lipid's accumulation, liver index, hepatic enzymes, collagen, hepatic oxidonitrative stress markers (like AOPP, MDA and NO2 -), and raised the levels of catalase (CAT) and superoxide dismutase (SOD) enzymes. Glutathione system components, namely glutathione (GSH), glutathione peroxidase (GPx), and glutathione-S-transferase (GST) levels were also restored in the safranal-treated groups. The reduction in serum TNF-α and IR provided further support to the anti-NAFLD effect of safranal. Moreover, the histopathological images indicated reverse of NAFLD activity score (NAS) through mild fatty degeneration, ballooning and inflammation in hepatocytes of treated groups.
Conclusion: Findings of blood and tissue analysis concluded that safranal can be a good choice in the management and cure of NAFLD.
Keywords: glutathione; inflammation; insulin resistance; non-alcoholic fatty liver disease; safranal.
© 2022 Sabir et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Usman Sabir reports grants from Higher Education Commission of Pakistan, during the conduct of the study; supporting project from Taif University Researchers Supporting Project number (TURSP-2020/78), Taif University, Taif, Saudi Arabia, outside the submitted work. The authors report no other potential conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Potential Hepatoprotective Effect of Matricaria Pubescens on High-Fat Diet-Induced Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Rats.Chem Biodivers. 2024 Apr;21(4):e202302005. doi: 10.1002/cbdv.202302005. Epub 2024 Mar 7. Chem Biodivers. 2024. PMID: 38451246
-
Voluntary oral feeding of rats not requiring a very high fat diet is a clinically relevant animal model of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD).Histol Histopathol. 2009 Sep;24(9):1161-9. doi: 10.14670/HH-24.1161. Histol Histopathol. 2009. PMID: 19609863
-
The Hepatic Antisteatosis Effect of Xanthohumol in High-Fat Diet-Fed Rats Entails Activation of AMPK as a Possible Protective Mechanism.Foods. 2023 Nov 22;12(23):4214. doi: 10.3390/foods12234214. Foods. 2023. PMID: 38231665 Free PMC article.
-
Free radical biology for medicine: learning from nonalcoholic fatty liver disease.Free Radic Biol Med. 2013 Dec;65:952-968. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2013.08.174. Epub 2013 Aug 29. Free Radic Biol Med. 2013. PMID: 23994574 Review.
-
Antioxidant Mechanisms in Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease.Curr Drug Targets. 2015;16(12):1301-14. doi: 10.2174/1389450116666150427155342. Curr Drug Targets. 2015. PMID: 25915484 Review.
Cited by
-
Utility of Human Relevant Preclinical Animal Models in Navigating NAFLD to MAFLD Paradigm.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Nov 25;23(23):14762. doi: 10.3390/ijms232314762. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36499091 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Effects of Chia Defatted Flour as a Nutritional Supplement in C57BL/6 Mice Fed a Low-Quality Diet.Foods. 2024 Feb 23;13(5):678. doi: 10.3390/foods13050678. Foods. 2024. PMID: 38472791 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of saffron, black seed, and their main constituents on inflammatory cytokine response (mainly TNF-α) and oxidative stress status: an aspect on pharmacological insights.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2023 Oct;396(10):2241-2259. doi: 10.1007/s00210-023-02501-w. Epub 2023 Apr 27. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37103518 Review.
-
Safranal Ameliorates Renal Damage, Inflammation, and Podocyte Injury in Membranous Nephropathy via SIRT/NF-κB Signalling.Curr Med Sci. 2025 Apr;45(2):288-300. doi: 10.1007/s11596-025-00020-8. Epub 2025 Mar 4. Curr Med Sci. 2025. PMID: 40035996 Free PMC article.
-
Exploration of the Key Genes Involved in Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Possible MicroRNA Therapeutic Targets.J Clin Exp Hepatol. 2024 Jul-Aug;14(4):101365. doi: 10.1016/j.jceh.2024.101365. Epub 2024 Feb 15. J Clin Exp Hepatol. 2024. PMID: 38433957 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Niederreiter L, Tilg H. Cytokines and fatty liver diseases. Liver Res. 2018;2(1):14–20. doi:10.1016/j.livres.2018.03.003 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

