Low-Dose Interleukin-2 Altered Gut Microbiota and Ameliorated Collagen-Induced Arthritis
- PMID: 35241924
- PMCID: PMC8887675
- DOI: 10.2147/JIR.S344393
Low-Dose Interleukin-2 Altered Gut Microbiota and Ameliorated Collagen-Induced Arthritis
Abstract
Purpose: Low-dose interleukin-2 (ld-IL-2) has been shown to regulate the balance between effector T and regulatory T (Treg) cells and has been used in several clinical trials to treat autoimmune diseases including rheumatoid arthritis (RA). In this study, we investigated the effects of ld-IL-2 on collagen-induced arthritis (CIA) in mice.
Methods: Arthritis severity in CIA mice was measured using the arthritis index (AI), radiographs, and hematoxylin and eosin staining. Cytokines were detected using enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Gut microbiota alterations and short-chain fatty acid production were analyzed through 16S rRNA sequencing and gas chromatography.
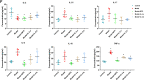
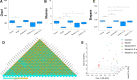
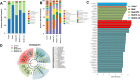
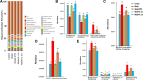
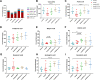
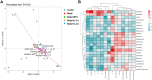
Results: The AI scores of CIA mice treated with ld-IL-2 were significantly lower compared to the model group, which significantly reduced the severity of arthritis. Ld-IL-2 also altered the gut microbiota in CIA mice. The diversity, composition, and dominant species of gut microbiota were altered by ld-IL-2 treatment. Ld-IL-2 also increased short-chain fatty acid levels. There was a strong correlation between ld-IL-2 treatment and improved gut microbiota.
Conclusion: Ld-IL-2 significantly ameliorated joint inflammation and bone damage and improved gut microbial dysbiosis in CIA, indicating that it may be a promising therapy for RA patients.
Keywords: 16sRNA; CIA; SCFA; gut microbiota; low-dose IL-2.
© 2022 Li et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Resistant starch intake alleviates collagen-induced arthritis in mice by modulating gut microbiota and promoting concomitant propionate production.J Autoimmun. 2021 Jan;116:102564. doi: 10.1016/j.jaut.2020.102564. Epub 2020 Nov 14. J Autoimmun. 2021. PMID: 33203617
-
Alteration of the gut microbiota in tumor necrosis factor-α antagonist-treated collagen-induced arthritis mice.Int J Rheum Dis. 2020 Apr;23(4):472-479. doi: 10.1111/1756-185X.13802. Epub 2020 Feb 26. Int J Rheum Dis. 2020. PMID: 32100456
-
Yanning Syrup ameliorates the lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammation: Adjusting the gut microbiota, short-chain fatty acids, and the CD4+ T cell balance.J Ethnopharmacol. 2022 Jan 30;283:114729. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2021.114729. Epub 2021 Oct 8. J Ethnopharmacol. 2022. PMID: 34634365
-
Protection against cartilage and bone destruction by systemic interleukin-4 treatment in established murine type II collagen-induced arthritis.Arthritis Res. 1999;1(1):81-91. doi: 10.1186/ar14. Epub 1999 Oct 26. Arthritis Res. 1999. PMID: 11056663 Free PMC article.
-
High-fat diet stimulated butyric acid metabolism dysbiosis, altered microbiota, and aggravated inflammatory response in collagen-induced arthritis rats.Nutr Metab (Lond). 2024 Nov 19;21(1):95. doi: 10.1186/s12986-024-00869-x. Nutr Metab (Lond). 2024. PMID: 39563394 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Restoring immune tolerance in pre-RA: immunometabolic dialogue between gut microbiota and regulatory T cells.Front Immunol. 2025 Mar 20;16:1565133. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1565133. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40181974 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Impact of lactobacillus probiotics on vaccine response in diabetic rats: modulation of inflammatory cytokines.Am J Clin Exp Immunol. 2025 Jun 15;14(3):157-166. doi: 10.62347/HUZJ9149. eCollection 2025. Am J Clin Exp Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40689314 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

