Effectiveness of Breathing Exercises, Foot Reflexology and Massage (BRM) on Maternal and Newborn Outcomes Among Primigravidae in Saudi Arabia: A Randomized Controlled Trial
- PMID: 35241937
- PMCID: PMC8887672
- DOI: 10.2147/IJWH.S347971
Effectiveness of Breathing Exercises, Foot Reflexology and Massage (BRM) on Maternal and Newborn Outcomes Among Primigravidae in Saudi Arabia: A Randomized Controlled Trial
Abstract
Background: Labor pain and anxiety are important concerns during labor, especially among the primigravidae. It may increase the duration of labor, increase stress hormones, and affect maternal and new-born related outcomes. This study examined the effectiveness of combined breathing exercises, foot reflexology, and massage (BRM) interventions on labor pain, anxiety, labor duration, stress hormone levels, maternal satisfaction, maternal vital signs, and the new-born's APGAR scores.
Participants and methods: This single-blind-parallel randomized controlled trial (RCT) was conducted at the Maternity and Children Hospital (MCH), Makkah, Saudi Arabia, by recruiting primigravidae aged 20 to 35 years, without any medical complications, and who were block-randomized at six-centimeter cervical dilation and stratified by intramuscular pethidine. The intervention is BRM compared to standard care. The labor pain was measured via present behavioral intensity (PBI) and visual analogue scale (VAS), and the anxiety was measured via Anxiety Assessment Scale for Pregnant Women in Labor (AASPWL). The secondary outcomes were duration of labor, maternal stress hormone levels, maternal vital signs, maternal satisfaction, fetal heart rate, and APGAR scores. All outcomes were measured at multiple time-points during and after contraction at baseline, during BRM intervention, at 60, 120, and 180 minutes post-intervention. Generalized linear mixed models were used to estimate the intervention effects over time.
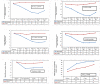
Results: A total of 225 participants were randomized for the control (n = 112) and intervention group (113). BRM lowered the labor pain intensity at 60 minutes after intervention during (1.3 vs 3.5, F = 102.5, p < 0.001) and after contraction (0.4 vs 2.4, F = 63.6, p < 0.001) and also lowered anxiety (2.9 vs 4.2, F = 80.4, p < 0.001). BRM correspondingly lowered adrenocorticotropic (ACTH) (133 vs 209 pg/mL, p < 0.001), cortisol (1231 vs 1360 nmol/mL, p = 0.003), and oxytocin (159 vs 121 pg/mL, p < 0.001). It also shortened the labor duration (165 vs 333 minutes, p < 0.001), improved vital signs, which resulted in higher APGAR scores, and increased maternal satisfaction.
Conclusion: The labor unit management could consider adopting BRM as one of the non-pharmacological analgesia for healthy women in labor.
Trial registration: ISRCTN87414969, registered 3 May 2019.
Keywords: breathing exercises; labor pain; massage; primigravidae; reflexology.
© 2022 Baljon et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Effectiveness of breathing exercises, foot reflexology and back massage (BRM) on labour pain, anxiety, duration, satisfaction, stress hormones and newborn outcomes among primigravidae during the first stage of labour in Saudi Arabia: a study protocol for a randomised controlled trial.BMJ Open. 2020 Jun 15;10(6):e033844. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2019-033844. BMJ Open. 2020. PMID: 32540887 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of foot reflexology massage on pregnant women: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled studies.Sci Rep. 2024 Jan 10;14(1):1012. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-51107-y. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38200035 Free PMC article.
-
The Effect of Foot Reflexology on Anxiety, Pain, and Outcomes of the Labor in Primigravida Women.Acta Med Iran. 2015 Aug;53(8):507-11. Acta Med Iran. 2015. PMID: 26545996 Clinical Trial.
-
Effectiveness of breathing exercises during the second stage of labor on labor pain and duration: a randomized controlled trial.J Integr Med. 2017 Nov;15(6):456-461. doi: 10.1016/S2095-4964(17)60368-6. J Integr Med. 2017. PMID: 29103415 Clinical Trial.
-
[Efficacy and delivery outcomes of women underwent double-catheter epidural block during labor].Zhonghua Fu Chan Ke Za Zhi. 2010 Nov;45(11):819-24. Zhonghua Fu Chan Ke Za Zhi. 2010. PMID: 21211279 Clinical Trial. Chinese.
Cited by
-
The most appropriate cervical dilatation for massage to reduce labor pain and anxiety: a randomized clinical trial.BMC Womens Health. 2022 Jul 7;22(1):282. doi: 10.1186/s12905-022-01864-1. BMC Womens Health. 2022. PMID: 35799221 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Effect of three modalities on emergence agitation among post-traumatic stress disorder patients undergoing laparoscopy: a randomized controlled study.BMC Psychiatry. 2024 Jan 29;24(1):78. doi: 10.1186/s12888-024-05525-5. BMC Psychiatry. 2024. PMID: 38281929 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Non-Pharmacological Pain Management in Labor: A Systematic Review.J Clin Med. 2023 Nov 21;12(23):7203. doi: 10.3390/jcm12237203. J Clin Med. 2023. PMID: 38068274 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Effects of Music-Based Interventions for Pain and Anxiety Management during Vaginal Labour and Caesarean Delivery: A Systematic Review and Narrative Synthesis of Randomised Controlled Trials.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2023 Nov 29;20(23):7120. doi: 10.3390/ijerph20237120. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2023. PMID: 38063550 Free PMC article.
-
The Effect of Chewing Gum in Managing Labor Pain Intensity and Anxiety Level in Primiparous Women: A Randomized Controlled Trial.Int J Community Based Nurs Midwifery. 2025 Apr 1;13(2):103-112. doi: 10.30476/ijcbnm.2025.102876.2515. eCollection 2025 Apr. Int J Community Based Nurs Midwifery. 2025. PMID: 40322058 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

