Synergistic Inhibition of Plantaricin E/F and Lactic Acid Against Aeromonas hydrophila LPL-1 Reveals the Novel Potential of Class IIb Bacteriocin
- PMID: 35242114
- PMCID: PMC8886044
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.774184
Synergistic Inhibition of Plantaricin E/F and Lactic Acid Against Aeromonas hydrophila LPL-1 Reveals the Novel Potential of Class IIb Bacteriocin
Abstract
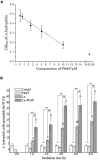
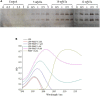
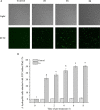
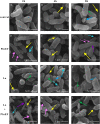
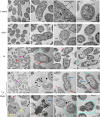
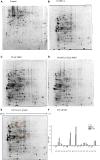
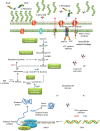
Plantaricin E/F (PlnEF) is a pair of two-component class IIb bacteriocin produced by lactic acid bacteria. PlnEF commonly displays potent antimicrobial activity against certain Gram-positive organisms. In this study, we investigated the synergistic activity of PlnEF combined with lactic acid against Gram-negative food and aquaculture potential pathogen Aeromonas hydrophila LPL-1, which is naturally resistant to PlnEF. We applied SDS-PAGE, wavelength-scanning, laser confocal microscopy, flow cytometer, scanning electron microscopy (SEM), transmission electron microscopy (TEM), and two-dimensional electrophoresis to investigate their synergistic inhibitory activities. The results showed that L-lactic acid drove the release of LPS from A. hydrophila, making it possible for PlnEF to contact the inner cell membrane of A. hydrophila. Besides, co-treatment of lactic acid and PlnEF caused severe morphological and intracellular changes of A. hydrophila, including blebs on the cell surface, abnormal cell elongation, inner membrane disruption, pore-forming through the outer and inner membrane, coagulation of the cytoplasm, and structural transformation of DNA. Protein profile analysis revealed that combined treatment of lactic acid and PlnEF inhibited the energy metabolism, protein synthesis, protein folding, and DNA replication in A. hydrophila. These findings proved that PlnEF combined with lactic acid was efficient against A. hydrophila and shed light on bacteriocin's potential and a new inhibition mechanism against A. hydrophila.
Importance: Bacteriocins and their producing strains are increasingly used to substitute artificial preservatives and antibiotics in the food and aquaculture industries. However, the bacteriocins produced by lactic acid bacteria are efficient to mainly Gram-positive bacteria. Our paper had demonstrated the antimicrobial activity of class IIb bacteriocin against potential Gram-negative pathogen, A. hydrophila LPL-1, when combined with lactic acid. The results could refresh our knowledge about the potential of class IIb bacteriocins produced by lactic acid bacteria.
Keywords: Gram-negative bacteria; bacteriocin; inhibition; lactic acid; lipopolysaccharide.
Copyright © 2022 Wang, Wei, Shang and Li.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Synergistic inhibition mechanism of pediocin PA-1 and L-lactic acid against Aeromonas hydrophila.Biochim Biophys Acta Biomembr. 2020 Oct 1;1862(10):183346. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamem.2020.183346. Epub 2020 May 16. Biochim Biophys Acta Biomembr. 2020. PMID: 32428447
-
Molecular characterisation of new organisation of plnEF and plw loci of bacteriocin genes harbour concomitantly in Lactobacillus plantarum I-UL4.Microb Cell Fact. 2015 Jun 16;14:89. doi: 10.1186/s12934-015-0280-y. Microb Cell Fact. 2015. PMID: 26077560 Free PMC article.
-
Two-peptide bacteriocin PlnEF causes cell membrane damage to Lactobacillus plantarum.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2016 Feb;1858(2):274-80. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamem.2015.11.018. Epub 2015 Nov 23. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2016. PMID: 26615918
-
Bacteriocins: modes of action and potentials in food preservation and control of food poisoning.Int J Food Microbiol. 1995 Dec;28(2):169-85. doi: 10.1016/0168-1605(95)00055-0. Int J Food Microbiol. 1995. PMID: 8750665 Review.
-
Recent Trends and Applications of Nanoencapsulated Bacteriocins against Microbes in Food Quality and Safety.Microorganisms. 2022 Dec 28;11(1):85. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms11010085. Microorganisms. 2022. PMID: 36677377 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Unraveling the antimicrobial potential of Lactiplantibacillus plantarum strains TE0907 and TE1809 sourced from Bufo gargarizans: advancing the frontier of probiotic-based therapeutics.Front Microbiol. 2024 Feb 14;15:1347830. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2024.1347830. eCollection 2024. Front Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 38419633 Free PMC article.
-
Palmatine Inhibits the Pathogenicity of Aeromonas hydrophila by Reducing Aerolysin Expression.Foods. 2022 Oct 18;11(20):3250. doi: 10.3390/foods11203250. Foods. 2022. PMID: 37430999 Free PMC article.
-
Characterisation of Enterocins Produced by Antilisterial Enterococcus faeciumBH04, BH12, BH84, and BH99 and In Vitro/In Situ Inhibition of Listeria monocytogenes.Food Sci Nutr. 2025 Apr 1;13(4):e70142. doi: 10.1002/fsn3.70142. eCollection 2025 Apr. Food Sci Nutr. 2025. PMID: 40177326 Free PMC article.
-
Administration of probiotics affects Artemia franciscana metanauplii intestinal ultrastructure and offers resistance against a Photobacterium damselae ssp. piscicida induced oxidative stress response.Fish Shellfish Immunol Rep. 2023 Aug 22;5:100113. doi: 10.1016/j.fsirep.2023.100113. eCollection 2023 Dec 15. Fish Shellfish Immunol Rep. 2023. PMID: 37671319 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Lactiplantibacillus plantarum LM1215 on Candida albicans and Gardnerella vaginalis.Yonsei Med J. 2024 Dec;65(12):727-740. doi: 10.3349/ymj.2023.0490. Yonsei Med J. 2024. PMID: 39609088 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abdulhussain Kareem R., Razavi S. H. (2020). Plantaricin bacteriocins: as safe alternative antimicrobial peptides in food preservation—A review. J. Food Saf. 40:e12735. 10.1111/jfs.12735 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

