Correlation Analysis and Intervention Study on Disturbance of Lipid Metabolism and Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy
- PMID: 35242203
- PMCID: PMC8888052
- DOI: 10.1155/2022/2579692
Correlation Analysis and Intervention Study on Disturbance of Lipid Metabolism and Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy
Retraction in
-
Retracted: Correlation Analysis and Intervention Study on Disturbance of Lipid Metabolism and Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy.Comput Math Methods Med. 2023 Jun 28;2023:9830307. doi: 10.1155/2023/9830307. eCollection 2023. Comput Math Methods Med. 2023. PMID: 37416230 Free PMC article.
Abstract
Objective: To explore the significance and clinical value of dynamic monitoring of lipid metabolism indexes in patients with diabetic peridiabetic lesions.
Methods: A total of 192 patients with type 2 diabetes (T2DM) treated in our hospital from October 2019 to July 2021 were divided into two groups according to whether they were complicated with peripheral neuropathy (DPN). The patients in the observation group were randomly assigned into group A (n = 45) and group B (n = 45) according to the method of random number table. The patients were assigned into control group (n = 102) and observation group (n = 90), and the patients in the observation group were randomly divided into two groups (n = 45). All the patients in the three groups were given routine hypoglycemic treatment, and group B was observed to dynamically monitor the indexes of lipid metabolism and regulate blood lipids on the basis of routine hypoglycemic treatment. The indexes of lipid metabolism, including total cholesterol (TC), triglyceride (TG), and high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C)/low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C), were detected before treatment. The receiver operating curve (ROC) was applied to elucidate the efficacy of TC, TG, and HDL-C and LDL-C in predicting peripheral neuropathy (DPN) in patients with T2DM. The indexes of lipid metabolism and neurological function of patients were determined after the treatment. The difference was considered to be statistically significant (P < 0.05).
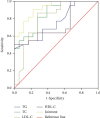
Results: In contrast to the control, the serum levels of TG, TC, and LDL-C in the observation group were significantly higher, with HDL-C significantly lower. ROC curve analysis indicated that the area under the curve (AUC) of serum TG level to predict peripheral neuropathy in patients with T2DM was 0.753 (95% CI = 0.604 - 0.901, P = 0.007). When the Youden index reached the maximum (0.677), with corresponding sensitivity and specificity 77.18% and 82.58%, respectively, and the critical value was 2.31 mmol/L, the AUC of serum TC level for predicting peripheral neuropathy in patients with T2DM was 0.851 (95% CI = 0.735 ~ 0.967P < 0.001); when the Youden index reaches its maximum (0.750), with the sensitivity and specificity 84.44% and 92.06%, respectively, and the critical value is 4.52 mmol/L, the AUC of predicting peripheral neuropathy in patients with T2DM by serum LDL-C level was 0.799 (95% CI = 0.52 ~ 0.946, P = 0.001); when the Youden index reaches its maximum (0.706), with sensitivity and specificity 80.58% and 87.24%, respectively, and the critical value is 3.36 mmol/L, the AUC of serum HDL-C level for predicting DPN in patients with T2DM was 0.727 (95% CI = 0.568 ~ 0.886P = 0.014). When the Youden index reached the maximum (0.640), the sensitivity and specificity were 74.56% and 83.25%, respectively, the critical value is 1.51 mmol/L. The AUC in predicting DPN in patients with T2DM was 0.919 (95% CI = 0.839 ~ 0.978P < 0.001); when the Jordan index reached the maximum (0.786), the sensitivity and specificity were 91.75% and 95.82%, respectively. Compared with group A, the levels of serum TG, TC, and LDL-C in group B decreased significantly, while the level of HDL-C increased (P < 0.05). The motor nerve conduction velocity and sensory nerve conduction velocity of median nerve and peroneal nerve in group B were higher than those in group A (P < 0.05).
Conclusion: Diabetic patients with severe lipid metabolic disorders have a higher risk of DPN. Combined detection of lipid metabolism indexes such as TC, TG, and HDL-C and LDL-C is effective in predicting diabetic patients with DPN. In clinic, through dynamic monitoring of lipid metabolism indexes, we can actively regulate the level of blood lipids in patients with T2DM, which can delay the occurrence and development of DPN to a certain extent, as well as improving the prognosis of patients with diabetes.
Copyright © 2022 Wei Wang et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Saeedi P., Petersohn I., Salpea P., et al. Global and regional diabetes prevalence estimates for 2019 and projections for 2030 and 2045: results from the international diabetes federation diabetes atlas, 9th edition. Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice . 2019;157(4, article 107843) doi: 10.1016/j.diabres.2019.107843. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Castelli G., Desai K. M., Cantone R. E. Peripheral neuropathy: evaluation and differential diagnosis. American Family Physician . 2020;102(12):732–739. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous