Human Decidual Mesenchymal Stem Cells Obtained From Early Pregnancy Improve Cardiac Revascularization Postinfarction by Activating Ornithine Metabolism
- PMID: 35242829
- PMCID: PMC8887417
- DOI: 10.3389/fcvm.2022.837780
Human Decidual Mesenchymal Stem Cells Obtained From Early Pregnancy Improve Cardiac Revascularization Postinfarction by Activating Ornithine Metabolism
Abstract
Background: Compared with bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells (BMSCs), decidual mesenchymal stem cells (DMSCs) are easy to obtain and exhibit excellent angiogenic effects, but their role in cell transplantation after myocardial infarction (MI) remains unclear.
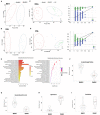
Methods: BMSCs and DMSCs were harvested from healthy donors. The effects of both cell types on angiogenesis were observed in vitro. Metabonomics analysis was performed to compare different metabolites and screen critical metabolic pathways. A murine model of acute myocardial infarction (AMI) was established, which was randomized into five groups (control, BMSC, DMSC, DMSC + ODCshRNA and BMSC + ODC consisting of 50 animals, equally divided into each group). The therapeutic effect of DMSCs on MI in rats was assessed based on neovascularization and cardiac remodeling.
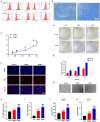
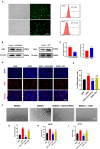
Results: DMSCs exhibited a better angiogenic effect on human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs) than BMSCs in vitro. In addition, ornithine metabolism, which is associated with vascularization, was significantly increased in DMSCs. The transplantation of DMSCs in the rat MI model significantly enhanced angiogenesis of the infarct border area and improved cardiac remodeling and dysfunction postinfarction compared with BMSCs. Furthermore, inhibition of ornithine metabolism by silencing ornithine decarboxylase (ODC) in DMSCs partly abolished the benefits of DMSC transplantation.
Conclusion: Compared with BMSCs, DMSCs exhibited better efficacy in improving revascularization and heart remodeling post-MI via the activation of ODC-associated ornithine metabolism.
Keywords: bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells; decidual mesenchymal stem cells; heart remodeling; ischemic heart disease; ornithine decarboxylase; revascularization.
Copyright © 2022 Chen, Bai, Lu, Chen, Liu, Guo, Qin, Jiao, Huang and Tian.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Human decidual mesenchymal stem cells obtained from early pregnancy attenuate bleomycin-induced lung fibrosis by inhibiting inflammation and apoptosis.Int Immunopharmacol. 2024 Dec 5;142(Pt B):113224. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2024.113224. Epub 2024 Sep 21. Int Immunopharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39306886
-
Bone-derived Nestin-positive mesenchymal stem cells improve cardiac function via recruiting cardiac endothelial cells after myocardial infarction.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2019 Apr 27;10(1):127. doi: 10.1186/s13287-019-1217-x. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2019. PMID: 31029167 Free PMC article.
-
Decidual mesenchymal stem/stromal cells from preeclamptic patients secrete endoglin, which at high levels inhibits endothelial cell attachment invitro.Placenta. 2022 Aug;126:175-183. doi: 10.1016/j.placenta.2022.07.003. Epub 2022 Jul 7. Placenta. 2022. PMID: 35853410
-
Low-dose aspirin treatment enhances the adhesion of preeclamptic decidual mesenchymal stem/stromal cells and reduces their production of pro-inflammatory cytokines.J Mol Med (Berl). 2018 Nov;96(11):1215-1225. doi: 10.1007/s00109-018-1695-9. Epub 2018 Oct 1. J Mol Med (Berl). 2018. PMID: 30276549
-
A brief review: the therapeutic potential of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells in myocardial infarction.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2017 Nov 2;8(1):242. doi: 10.1186/s13287-017-0697-9. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2017. PMID: 29096705 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Maternal Supplementation with Ornithine Promotes Placental Angiogenesis and Improves Intestinal Development of Suckling Piglets.Animals (Basel). 2024 Feb 22;14(5):689. doi: 10.3390/ani14050689. Animals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38473074 Free PMC article.
-
Co-treatment with bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells and curcumin improved angiogenesis in myocardium in a rat model of MI.Mol Biol Rep. 2024 Feb 1;51(1):261. doi: 10.1007/s11033-023-09180-z. Mol Biol Rep. 2024. PMID: 38302805
-
Insufficient S-adenosylhomocysteine hydrolase compromises the beneficial effect of diabetic BMSCs on diabetic cardiomyopathy.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2022 Aug 13;13(1):418. doi: 10.1186/s13287-022-03099-1. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2022. PMID: 35964109 Free PMC article.
-
Ultrasound‑targeted microbubble destruction technology delivering β‑klotho to the heart enhances FGF21 sensitivity and attenuates heart remodeling post‑myocardial infarction.Int J Mol Med. 2024 Jun;53(6):54. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2024.5378. Epub 2024 Apr 26. Int J Mol Med. 2024. PMID: 38666537 Free PMC article.
-
Applications of extraembryonic tissue-derived cells in vascular tissue regeneration.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2024 Jul 9;15(1):205. doi: 10.1186/s13287-024-03784-3. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2024. PMID: 38982541 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Meyer GP, Wollert KC, Lotz J, Steffens J, Lippolt P, Fichtner S, et al. . Intracoronary bone marrow cell transfer after myocardial infarction: eighteen months' follow-up data from the randomized, controlled boost (bone marrow transfer to enhance st-elevation infarct regeneration) trial. Circulation. (2006) 113:1287–94. 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.105.575118 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

