Exosomal myeloperoxidase as a biomarker of deep venous thrombosis
- PMID: 35242854
- PMCID: PMC8825553
- DOI: 10.21037/atm-21-5583
Exosomal myeloperoxidase as a biomarker of deep venous thrombosis
Abstract
Background: Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) often occurs following major orthopedic surgery. In this study, we investigated specific exosomal proteins as potential diagnostic biomarkers of DVT.
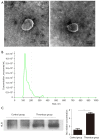
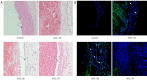
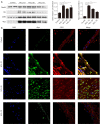
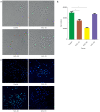
Methods: Proteomic analysis of exosomes from four DVT patients and healthy controls (n=4) was performed by mass spectrometry. The model animals were evaluated at 1 inferior vena cava ligation [(IVCL)-1D], 3 (IVCL-3D), and 7 (IVCL-7D) days after IVCL. Endothelial cells in the thrombus segment were examined using terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase dUTP nick end labeling (TUNEL) assays and hematoxylin and eosin (HE) staining. Myeloperoxidase (MPO) expression in the damaged vessel was detected by immunofluorescence staining. Exosomes were co-cultured with human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs) and cell proliferation was estimated using Cell Counting Kit-8 (CCK-8) assays.
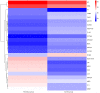
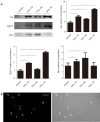
Results: A total of 78 differentially expressed proteins (DEPs; 38 downregulated and 40 upregulated) were identified in the DVT group. In the rat DVT model, endothelial cells were damaged continuously after thrombosis, with the most serious injury in the IVCL-3D group, after which signs of endothelial repair were apparent. The IVCL-1D group showed the highest levels of vascular endothelial cell apoptosis and MPO increased sharply in the IVCL-1D and IVCL-3D groups, but had almost disappeared in the IVCL-7D group. In co-culture, plasma exosomes isolated from DVT model rats were efficiently absorbed by HUVECs, with markedly lower HUVECs growth and higher levels of apoptosis in the IVCL-1D and IVCL-3D groups compared with the control group.
Conclusions: Our findings suggest that exosomes may be involved in endothelial cell injury during DVT. The exosomal protein MPO is a potential biomarker of early stage DVT.
Keywords: Exosomes; deep vein thrombosis (DVT); myeloperoxidase; proteomic analysis.
2022 Annals of Translational Medicine. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form (available at https://dx.doi.org/10.21037/atm-21-5583). The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Upregulated miR-206 Aggravates Deep Vein Thrombosis by Regulating GJA1-Mediated Autophagy of Endothelial Progenitor Cells.Cardiovasc Ther. 2022 Mar 18;2022:9966306. doi: 10.1155/2022/9966306. eCollection 2022. Cardiovasc Ther. 2022. PMID: 35360546 Free PMC article.
-
Bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells accelerate angiogenesis in pregnant experimentally induced deep venous thrombosis rat model via up-regulation of pro-angiogenic secretogranin II.Int Immunopharmacol. 2023 May;118:110025. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2023.110025. Epub 2023 Mar 16. Int Immunopharmacol. 2023. PMID: 36933488
-
ET1 acts as a potential plasma biomarker and therapeutic target in deep venous thrombosis rat model.J Thromb Thrombolysis. 2024 Aug;57(6):1067-1075. doi: 10.1007/s11239-024-02981-4. Epub 2024 Jun 2. J Thromb Thrombolysis. 2024. PMID: 38824487 Free PMC article.
-
Peroxisome proliferator‑activated receptor γ alleviates human umbilical vein endothelial cell injury in deep vein thrombosis by blocking endoplasmic reticulum stress.Exp Ther Med. 2024 Aug 1;28(4):385. doi: 10.3892/etm.2024.12674. eCollection 2024 Oct. Exp Ther Med. 2024. PMID: 39161618 Free PMC article.
-
Elevated miR-195-5p expression in deep vein thrombosis and mechanism of action in the regulation of vascular endothelial cell physiology.Exp Ther Med. 2019 Dec;18(6):4617-4624. doi: 10.3892/etm.2019.8166. Epub 2019 Nov 4. Exp Ther Med. 2019. PMID: 31807149 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Quantitative proteomic analysis of circulating exosomes reveals the mechanism by which Triptolide protects against collagen-induced arthritis.Immun Inflamm Dis. 2024 Jun;12(6):e1322. doi: 10.1002/iid3.1322. Immun Inflamm Dis. 2024. PMID: 38888462 Free PMC article.
-
Single molecule array measures of LRRK2 kinase activity in serum link Parkinson's disease severity to peripheral inflammation.Mol Neurodegener. 2024 Jun 11;19(1):47. doi: 10.1186/s13024-024-00738-4. Mol Neurodegener. 2024. PMID: 38862989 Free PMC article.
-
Recent Advances on the Molecular Mechanism and Clinical Trials of Venous Thromboembolism.J Inflamm Res. 2023 Dec 14;16:6167-6178. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S439205. eCollection 2023. J Inflamm Res. 2023. PMID: 38111686 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exosomes in Central Nervous System Diseases: A Comprehensive Review of Emerging Research and Clinical Frontiers.Biomolecules. 2024 Nov 27;14(12):1519. doi: 10.3390/biom14121519. Biomolecules. 2024. PMID: 39766226 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hypochlorous acid derived from microglial myeloperoxidase could mediate high-mobility group box 1 release from neurons to amplify brain damage in cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury.J Neuroinflammation. 2024 Mar 21;21(1):70. doi: 10.1186/s12974-023-02991-8. J Neuroinflammation. 2024. PMID: 38515139 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
