DNA G-quadruplexes are uniquely stable in the presence of denaturants and monovalent cations
- PMID: 35243016
- PMCID: PMC8885576
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbrep.2022.101238
DNA G-quadruplexes are uniquely stable in the presence of denaturants and monovalent cations
Abstract
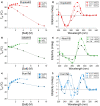
Ions in the Hofmeister series exhibit varied effects on biopolymers. Those classed as kosmotropes generally stabilize secondary structure, and those classed as chaotropes generally destabilize secondary structure. Here, we report that several anionic chaotropes exhibit unique effects on one DNA secondary structure - a G quadruplex. These chaotropes exhibit the expected behaviour (destabilization of secondary structure) in two other structural contexts: a DNA duplex and i-Motifs. Uniquely among secondary structures, we observe that G quadruplexes are comparatively insensitive to the presence of anionic chaotropes, but not other denaturants. Further, the presence of equimolar NaCl provided greater mitigation of the destabilization caused by other non-anionic denaturants. These results are consistent with the presence of monovalent cations providing an especially pronounced stabilizing effect to G quadruplexes when studied in denaturing solution conditions.
Keywords: DNA; Denaturant; G quadruplex; Hofmeister; Nucleic acids.
© 2022 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts to declare.
Figures



References
-
- Zhang Y., Cremer P.S. Interactions between macromolecules and ions: the Hofmeister series. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2006;10:658–663. - PubMed
-
- Talib J., Green C., Davis K.J., Urathamakul T., Beck J.L., Aldrich-Wright J.R., Ralph S.F. A comparison of the binding of metal complexes to duplex and quadruplex DNA. Dalton Trans. 2008:1018–1026. - PubMed
-
- Stefan L., Monchaud D. Applications of guanine quartets in nanotechnology and chemical biology. Nat. Rev. Chem. 2019;3:650–668.
-
- Salis A., Bilanicova D., Ninham B.W., Monduzzi M. Hofmeister effects in enzymatic activity: weak and strong electrolyte influences on the activity of Candida rugosa lipase. J. Phys. Chem. B. 2007;111:1149–1156. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

