Trial-based Cost-effectiveness Analysis of an Immediate Postoperative Mitomycin C Instillation in Patients with Non-muscle-invasive Bladder Cancer
- PMID: 35243387
- PMCID: PMC8883187
- DOI: 10.1016/j.euros.2021.12.008
Trial-based Cost-effectiveness Analysis of an Immediate Postoperative Mitomycin C Instillation in Patients with Non-muscle-invasive Bladder Cancer
Abstract
Background: Bladder cancer imposes a significant public health burden on the European Union. There is a need for cost-effective treatment and follow-up regimens.
Objective: To assess the cost-effectiveness of immediate mitomycin C (MMC) instillation within 1 d after surgery compared to delayed MMC instillation within 2 wk after surgery with further adjuvant treatment, depending on the patient's risk group.
Design setting and participants: This economic evaluation was based on a randomized controlled trial among 2243 Dutch patients with non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer (NMIBC) patients from a health care perspective over a 3-yr time period.
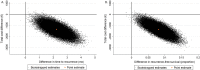
Outcome measurements and statistical analysis: The treatment effect was measured as time to recurrence and recurrence-free survival. Missing effect data were imputed with multiple imputation. Health care utilization and related costs were estimated on the basis of treatment protocols for NMIBC patients in the Netherlands. Statistical uncertainty was estimated using bootstrapping and is graphically presented using cost-effectiveness planes and cost-effectiveness acceptability curves.
Results and limitations: Time to recurrence was significantly longer for immediate MMC instillation (27.31 mo) than for delayed MMC instillation (24.97 mo), with an adjusted mean difference of 2.21 mo (95% confidence interval [CI] 1.58-2.84). The proportion of patients with recurrence-free survival was significantly higher after immediate MMC instillation (0.65) than after delayed MMC instillation (0.56), with an adjusted mean difference of 0.08 (95% CI 0.06-0.11). Total mean health care costs per patient were significantly lower for immediate MMC instillation (€22 959) than for delayed MMC instillation (€24 624), with an adjusted mean difference of -€1350 (95% CI -€1799 to -€900). The study is limited by the retrospective estimation of costs.
Conclusions: This trial-based cost-effectiveness analysis shows that from a health care perspective, immediate MMC instillation is more effective and less expensive compared to delayed MMC instillation.
Patient summary: We assessed the cost-effectiveness of immediate bladder instillation of mitomycin C after surgery to reduce the risk of recurrence after removal of the bladder tumor as compared to delayed instillation in a large Dutch population of patients with non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer. We found that immediate instillation was more effective and less expensive than delayed instillation. We conclude that immediate mitomycin C instillation is a cost-effective treatment for non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer.
Keywords: Cost-effectiveness; Intravesical chemotherapy; Mitomycin C; Non–muscle-invasive bladder cancer.
© 2021 The Author(s).
Figures
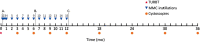
References
-
- Leal J., Luengo-Fernandez R., Sullivan R., Witjes J.A. Economic burden of bladder cancer across the European Union. Eur Urol. 2016;69:438–447. - PubMed
-
- Svatek R.S., Hollenbeck B.K., Holmäng S., et al. The economics of bladder cancer: costs and considerations of caring for this disease. Eur Urol. 2014;66:253–262. - PubMed
-
- Babjuk M., Burger M., Compérat E.M., et al. European Association of Urology guidelines on non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer (TaT1 and carcinoma in situ)—2019 update. Eur Urol. 2019;76:639–657. - PubMed
-
- Bosschieter J., Nieuwenhuijzen J.A., van Ginkel T., et al. Value of an immediate intravesical instillation of mitomycin C in patients with non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer: a prospective multicentre randomised study in 2243 patients. Eur Urol. 2018;73:226–232. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

