Engineered Living Hydrogels
- PMID: 35243704
- PMCID: PMC9250645
- DOI: 10.1002/adma.202201326
Engineered Living Hydrogels
Abstract
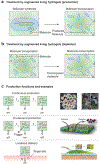
Living biological systems, ranging from single cells to whole organisms, can sense, process information, and actuate in response to changing environmental conditions. Inspired by living biological systems, engineered living cells and nonliving matrices are brought together, which gives rise to the technology of engineered living materials. By designing the functionalities of living cells and the structures of nonliving matrices, engineered living materials can be created to detect variability in the surrounding environment and to adjust their functions accordingly, thereby enabling applications in health monitoring, disease treatment, and environmental remediation. Hydrogels, a class of soft, wet, and biocompatible materials, have been widely used as matrices for engineered living cells, leading to the nascent field of engineered living hydrogels. Here, the interactions between hydrogel matrices and engineered living cells are described, focusing on how hydrogels influence cell behaviors and how cells affect hydrogel properties. The interactions between engineered living hydrogels and their environments, and how these interactions enable versatile applications, are also discussed. Finally, current challenges facing the field of engineered living hydrogels for their applications in clinical and environmental settings are highlighted.
Keywords: engineered living hydrogels; microbe-material interactions; real-world applications; synthetic biology.
© 2022 Wiley-VCH GmbH.
Figures












Similar articles
-
Programmable Morphing Hydrogels for Soft Actuators and Robots: From Structure Designs to Active Functions.Acc Chem Res. 2022 Jun 7;55(11):1533-1545. doi: 10.1021/acs.accounts.2c00046. Epub 2022 Apr 12. Acc Chem Res. 2022. PMID: 35413187
-
Protein-Based Hydrogels and Their Biomedical Applications.Molecules. 2023 Jun 25;28(13):4988. doi: 10.3390/molecules28134988. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 37446650 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Enzyme-Laden Bioactive Hydrogel for Biocatalytic Monitoring and Regulation.Acc Chem Res. 2021 Mar 2;54(5):1274-1287. doi: 10.1021/acs.accounts.0c00832. Epub 2021 Feb 11. Acc Chem Res. 2021. PMID: 33570397 Review.
-
Nanocellulose-based hydrogels as versatile materials with interesting functional properties for tissue engineering applications.J Mater Chem B. 2024 Aug 14;12(32):7692-7759. doi: 10.1039/d4tb00397g. J Mater Chem B. 2024. PMID: 38805188 Review.
-
3D Printing of Polysaccharide-Based Hydrogel Scaffolds for Tissue Engineering Applications: A Review.Int J Biol Macromol. 2024 Jun;270(Pt 2):132123. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2024.132123. Epub 2024 May 17. Int J Biol Macromol. 2024. PMID: 38761909 Review.
Cited by
-
Design and Development of Extracellular Matrix Protein-Based Microcapsules as Tools for Bacteria Investigation.Adv Healthc Mater. 2023 Apr;12(11):e2202789. doi: 10.1002/adhm.202202789. Epub 2023 Jan 16. Adv Healthc Mater. 2023. PMID: 36599129 Free PMC article.
-
Engineering living cells with cucurbit[7]uril-based supramolecular polymer chemistry: from cell surface engineering to manipulation of subcellular organelles.Chem Sci. 2022 Jul 6;13(30):8885-8894. doi: 10.1039/d2sc02797f. eCollection 2022 Aug 4. Chem Sci. 2022. PMID: 35975152 Free PMC article.
-
A roadmap for developing and engineering in vitro pulmonary fibrosis models.Biophys Rev (Melville). 2023 Apr 28;4(2):021302. doi: 10.1063/5.0134177. eCollection 2023 Jun. Biophys Rev (Melville). 2023. PMID: 38510343 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dynamic Hydrogels against Infections: From Design to Applications.Gels. 2024 May 14;10(5):331. doi: 10.3390/gels10050331. Gels. 2024. PMID: 38786248 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lignin-Based Mucus-Mimicking Antiviral Hydrogels with Enzyme Stability and Tunable Porosity.ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2025 Feb 12;17(6):8962-8975. doi: 10.1021/acsami.4c18519. Epub 2025 Jan 28. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2025. PMID: 39876589 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Flemming H-C, Wingender J, Szewzyk U, Steinberg P, Rice SA, Kjelleberg S, Nature Reviews Microbiology 2016, 14, 563. - PubMed
-
- Flemming H-C, Wingender J, Nature Reviews Microbiology 2010, 8, 623. - PubMed
-
- Tang T-C, An B, Huang Y, Vasikaran S, Wang Y, Jiang X, Lu TK, Zhong C, Nature Reviews Materials 2021, 6, 332.
-
- Rodrigo-Navarro A, Sankaran S, Dalby MJ, del Campo A, Salmeron-Sanchez M, Nature Reviews Materials 2021, 6, 1175.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

