Altered prefrontal signaling during inhibitory control in a salient drug context in cocaine use disorder
- PMID: 35244138
- PMCID: PMC9890460
- DOI: 10.1093/cercor/bhac087
Altered prefrontal signaling during inhibitory control in a salient drug context in cocaine use disorder
Abstract
Introduction: Drug addiction is characterized by impaired response inhibition and salience attribution (iRISA), where the salience of drug cues is postulated to overpower that of other reinforcers with a concomitant decrease in self-control. However, the neural underpinnings of the interaction between the salience of drug cues and inhibitory control in drug addiction remain unclear.
Methods: We developed a novel stop-signal functional magnetic resonance imaging task where the stop-signal reaction time (SSRT-a classical inhibitory control measure) was tested under different salience conditions (modulated by drug, food, threat, or neutral words) in individuals with cocaine use disorder (CUD; n = 26) versus demographically matched healthy control participants (n = 26).
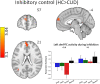
Results: Despite similarities in drug cue-related SSRT and valence and arousal word ratings between groups, dorsolateral prefrontal cortex (dlPFC) activity was diminished during the successful inhibition of drug versus food cues in CUD and was correlated with lower frequency of recent use, lower craving, and longer abstinence (Z > 3.1, P < 0.05 corrected).
Discussion: Results suggest altered involvement of cognitive control regions (e.g. dlPFC) during inhibitory control under a drug context, relative to an alternative reinforcer, in CUD. Supporting the iRISA model, these results elucidate the direct impact of drug-related cue reactivity on the neural signature of inhibitory control in drug addiction.
Keywords: craving; cue reactivity; dorsolateral prefrontal cortex; response inhibition; stop-signal task.
© The Author(s) 2022. Published by Oxford University Press. All rights reserved. For permissions, please e-mail: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures




References
-
- American Psychiatric Association , editors. Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders. 5th ed.: American Psychiatric Association; 2013
-
- Avants BB, Epstein CL, Grossman M, Gee JC. 2008. Symmetric diffeomorphic image registration with cross-correlation: evaluating automated labeling of elderly and neurodegenerative brain. Medical Image Analysis, Special Issue on the Third International Workshop on Biomedical Image Registration – WBIR 2006. 12:26–41. - PMC - PubMed

