The ascension of nanosponges as a drug delivery carrier: preparation, characterization, and applications
- PMID: 35244808
- PMCID: PMC8897344
- DOI: 10.1007/s10856-022-06652-9
The ascension of nanosponges as a drug delivery carrier: preparation, characterization, and applications
Abstract
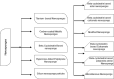
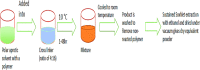
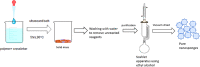
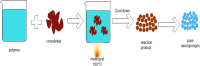
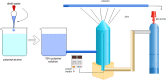
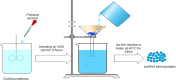
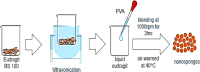
Nanosponges are nanosized drug carriers with a three-dimensional structure created by crosslinking polymers. They have the advantage of being able to hold a wide range of drugs of various sizes. Nanosponges come in a variety of shapes and sizes. They are distinguished by the research method used, the type of polymer used, and the type of drug they may contain. Nanosponges are superior to other delivery systems because they can provide a controlled drug release pattern with targeted drug delivery. The period of action, as well as the drug's residence time, may be regulated. Since it is made of biodegradable materials, it has a low toxicity and is safe to use. The efficiency of drug encapsulation is determined by the size of the drug molecule and the amount of void space available. Cancer, enzyme and biocatalyst carrier, oxygen delivery, solubility enhancement, enzyme immobilization, and poison absorbent are some of the applications for nanosponges. The method of preparation, characterization, factors affecting nanosponge development, drug loading and release mechanism, recent developments in this area, and patents filed in the area of nanosponges are all highlighted in this study. Graphical abstract.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Cyclodextrin based nanosponges for pharmaceutical use: a review.Acta Pharm. 2013 Sep;63(3):335-58. doi: 10.2478/acph-2013-0021. Acta Pharm. 2013. PMID: 24152895 Review.
-
Nanosponges- Versatile Platform as Drug Carrier.Recent Pat Nanotechnol. 2023;17(2):91-103. doi: 10.2174/1872210516666220905092202. Recent Pat Nanotechnol. 2023. PMID: 36748244 Review.
-
Ester-Based Hydrophilic Cyclodextrin Nanosponges for Topical Ocular Drug Delivery.Curr Pharm Des. 2016;22(46):6988-6997. doi: 10.2174/1381612822666161216113207. Curr Pharm Des. 2016. PMID: 27981908
-
Evolving Era of "Sponges": Nanosponges as a Versatile Nanocarrier for the Effective Skin Delivery of Drugs.Curr Pharm Des. 2022;28(23):1885-1896. doi: 10.2174/1381612828666220518090431. Curr Pharm Des. 2022. PMID: 35585809 Review.
-
Multifunctional Drug Delivery System: Nanosponges.Recent Pat Nanotechnol. 2025;19(3):319-335. doi: 10.2174/0118722105246668231012113121. Recent Pat Nanotechnol. 2025. PMID: 37916495 Review.
Cited by
-
Nanosponges: An overlooked promising strategy to combat SARS-CoV-2.Drug Discov Today. 2022 Oct;27(10):103330. doi: 10.1016/j.drudis.2022.07.015. Epub 2022 Jul 28. Drug Discov Today. 2022. PMID: 35908684 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Nanorobotics-Based Approach of Breast Cancer in the Nanotechnology Era.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 May 2;25(9):4981. doi: 10.3390/ijms25094981. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38732200 Free PMC article. Review.
-
In vitro and preclinical evaluation of the antifungal activity of 6-methoxy-1 H-indole-2-carboxylic acid produced by Bacillus toyonensis strain OQ071612 formulated as nanosponge hydrogel.Microb Cell Fact. 2025 Apr 1;24(1):77. doi: 10.1186/s12934-025-02688-y. Microb Cell Fact. 2025. PMID: 40169999 Free PMC article.
-
Nanosponges for Drug Delivery and Cancer Therapy: Recent Advances.Nanomaterials (Basel). 2022 Jul 16;12(14):2440. doi: 10.3390/nano12142440. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35889665 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Fabrication, characterization, and docking studies of furosemide-loaded nanosponges using the emulsion solvent diffusion method.Nanomedicine (Lond). 2025 Jun;20(11):1235-1247. doi: 10.1080/17435889.2025.2501518. Epub 2025 May 7. Nanomedicine (Lond). 2025. PMID: 40329918
References
-
- Mali AD, Bathe R, Patil M. An updated review on transdermal drug delivery systems. Int J Adv Sci Res. 2015;1:244. doi: 10.7439/ijasr.v1i6.2243. - DOI
-
- Soares PIP, Romão J, Matos R, Silva JC, Borges JP. Design and engineering of magneto-responsive devices for cancer theranostics: Nano to macro perspective. Prog Mater Sci. 2021;116:100742. doi: 10.1016/j.pmatsci.2020.100742. - DOI
-
- Nanotechnology in Textiles: theory and application - Rajesh Mishra, Jiri Militky - Google Books p.80, n.d. https://books.google.co.in/books?hl=en&lr=&id=4WR6DwAAQBAJ&oi=fnd&pg=PA1.... Accessed 19 Feb 2021
-
- Wei T, Torkelson JM. Molecular weight dependence of the glass transition temperature (Tg)-confinement effect in well-dispersed poly(2-vinyl pyridine)-silica nanocomposites: comparison of interfacial layer tgand matrix Tg. Macromolecules. 2020;53:8725–36. doi: 10.1021/acs.macromol.0c01577. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources