Exercise Training and Natural Killer Cells in Cancer Survivors: Current Evidence and Research Gaps Based on a Systematic Review and Meta-analysis
- PMID: 35244811
- PMCID: PMC8897541
- DOI: 10.1186/s40798-022-00419-w
Exercise Training and Natural Killer Cells in Cancer Survivors: Current Evidence and Research Gaps Based on a Systematic Review and Meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: Exercise training can positively impact the immune system and particularly natural killer (NK) cells, at least in healthy people. This effect would be of relevance in the context of cancer given the prominent role of these cells in antitumor immunity. In this systematic review and meta-analysis, we aimed to summarize current evidence on the effects of exercise training on the levels and function of NK cells in cancer survivors (i.e., from the time of diagnosis until the end of life).
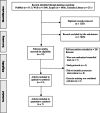
Methods: Relevant articles were searched in PubMed, Scopus, Web of Science and Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials (until January 11, 2022). Randomized controlled trials (RCT) of exercise training (i.e., non-acute) interventions vs usual care conducted in cancer survivors and assessing NK number and/or cytotoxic activity (NKCA) before and upon completion of the intervention were included. Methodological quality of the studies was assessed with the PEDro scale, and results were meta-analyzed using a random effects (Dersimoian and Laird) model.
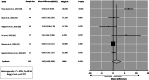
Results: Thirteen RCT including 459 participants (mean age ranging 11-63 years) met the inclusion criteria. Methodological quality of the studies was overall fair (median PEDro score = 5 out of 10). There was heterogeneity across studies regarding cancer types (breast cancer, non-small cell lung cancer and other solid tumors), treatment (e.g., receiving vs having received chemotherapy), exercise modes (aerobic or resistance exercise, Tai Chi, Yoga) and duration (2-24 weeks). No consistent effects were observed for NK number in blood (mean difference [MD]: 1.47, 95% confidence interval [CI] - 0.35 to 3.29, p = 0.113) or NKCA as assessed in vitro (MD: - 0.02, 95%CI - 0.17 to 0.14, p = 0.834). However, mixed results existed across studies, and some could not be meta-analyzed due to lack of information or methodological heterogeneity.
Conclusions: Current evidence does not support a significant effect of exercise training intervention on NK cells in blood or on their 'static response' (as assessed in vitro) in cancer survivors. Several methodological issues and research gaps are highlighted in this review, which should be considered in future studies to draw definite conclusions on this topic.
Keywords: Cytotoxic activity; Immune function; Immune system; Immunity; Oncology; Physical activity; Training.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Pedro Valenzuela, Gonzalo Saco-Ledo, Alejandro Santos-Lozano, Javier Morales, Adrián Castillo-García, Richard Simpson, Alejandro Lucia and Carmen Fiuza-Luces declare that they have no conflicts of interest relevant to the content of this review.
Figures

References
-
- Walsh NP, Gleeson M, Shephard RJ, Gleeson M, Woods JA, Bishop NC, et al. Position statement. Part one: immune function and exercise. Exerc Immunol Rev. 2011;17:6–63. - PubMed
-
- Kruijsen-Jaarsma M, Révész D, Bierings MB, Buffart LM, Takken T. Effects of exercise on immune function in patients with cancer: a systematic review. Exerc Immunol Rev. 2013;19:120–143. - PubMed
-
- Timmons BW, Cieslak T. Human natural killer cell subsets and acute exercise: a brief review. Exerc Immunol Rev. 2008;14:8–23. - PubMed
-
- Rincón HG, Solomon GF, Benton D, Rubenstein LZ. Exercise in frail elderly men decreases natural killer cell activity. Aging Clin Exp Res. 1996;8:109–112. - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

