Diacerein counteracts acetaminophen-induced hepatotoxicity in mice via targeting NLRP3/caspase-1/IL-1β and IL-4/MCP-1 signaling pathways
- PMID: 35244883
- PMCID: PMC8967791
- DOI: 10.1007/s12272-022-01373-7
Diacerein counteracts acetaminophen-induced hepatotoxicity in mice via targeting NLRP3/caspase-1/IL-1β and IL-4/MCP-1 signaling pathways
Abstract
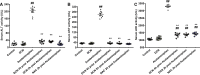
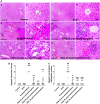
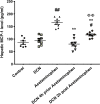
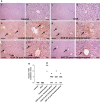
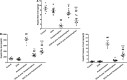
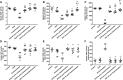
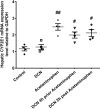
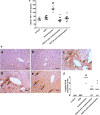
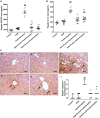
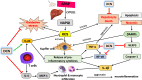
The current study aims at repurposing the anti-arthritic drug diacerein (DCN) for the treatment of acetaminophen hepatotoxicity and investigating the potential underlying mechanisms. Mice were randomly divided into six groups receiving either no treatment (control group), 20 mg/kg DCN i.p, 400 mg/kg acetaminophen i.p, DCN 4 h before acetaminophen, DCN 2 h after acetaminophen, or 400 mg/kg N-acetylcysteine (NAC) i.p, 2 h after acetaminophen. Biomarkers of liver dysfunction, oxidative stress, and apoptosis were assessed. Hepatic necroinflammatory changes were evaluated along with hepatic expression of NF-κB and caspase-1. The levels of NLRP3, IL-1β, IL-4, MCP-1, and TNF-α in the liver, as well as CYP2E1 mRNA expression, were measured. Diacerein significantly reduced biomarkers of liver dysfunction, oxidative stress, hepatocyte necrosis, and infiltration of neutrophils and macrophages whether administered 4 h before or 2 h after acetaminophen. Further, the effects were comparable to those of NAC. Diacerein also counteracted acetaminophen-induced hepatocellular apoptosis by increasing Bcl-2 and decreasing Bax and caspase-3 expression levels. Moreover, DCN normalized hepatic TNF-α and significantly decreased NF-κB p65 expression. Accordingly, DCN can prevent or reverse acetaminophen hepatotoxicity in mice, suggesting potential utility as a repurposed drug for clinical treatment.
Keywords: Acetaminophen; Diacerein; IL-1β; IL-4; MCP-1; NLRP3.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

