Periodontitis and cardiometabolic disorders: The role of lipopolysaccharide and endotoxemia
- PMID: 35244966
- PMCID: PMC9314839
- DOI: 10.1111/prd.12433
Periodontitis and cardiometabolic disorders: The role of lipopolysaccharide and endotoxemia
Abstract
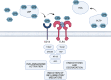
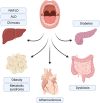
Lipopolysaccharide is a virulence factor of gram-negative bacteria with a crucial importance to the bacterial surface integrity. From the host's perspective, lipopolysaccharide plays a role in both local and systemic inflammation, activates both innate and adaptive immunity, and can trigger inflammation either directly (as a microbe-associated molecular pattern) or indirectly (by inducing the generation of nonmicrobial, danger-associated molecular patterns). Translocation of lipopolysaccharide into the circulation causes endotoxemia, which is typically measured as the biological activity of lipopolysaccharide to induce coagulation of an aqueous extract of blood cells of the assay. Apparently healthy subjects have a low circulating lipopolysaccharide activity, since it is neutralized and cleared rapidly. However, chronic endotoxemia is involved in the pathogenesis of many inflammation-driven conditions, especially cardiometabolic disorders. These include atherosclerotic cardiovascular diseases, obesity, liver diseases, diabetes, and metabolic syndrome, where endotoxemia has been recognized as a risk factor. The main source of endotoxemia is thought to be the gut microbiota. However, the oral dysbiosis in periodontitis, which is typically enriched with gram-negative bacterial species, may also contribute to endotoxemia. As endotoxemia is associated with an increased risk of cardiometabolic disorders, lipopolysaccharide could be considered as a molecular link between periodontal microbiota and cardiometabolic diseases.
Keywords: microbiota; mouth; oral infections; oral inflammation; plaque; saliva.
© 2022 The Authors. Periodontology 2000 published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Mediators between oral dysbiosis and cardiovascular diseases.Eur J Oral Sci. 2018 Oct;126 Suppl 1:26-36. doi: 10.1111/eos.12423. Eur J Oral Sci. 2018. PMID: 30178551 Review.
-
Gut barrier dysfunction and endotoxemia in heart failure: A dangerous connubium?Am Heart J. 2023 Oct;264:40-48. doi: 10.1016/j.ahj.2023.06.002. Epub 2023 Jun 9. Am Heart J. 2023. PMID: 37301317 Review.
-
Gut microbial dysbiosis and inflammation: Impact on periodontal health.J Periodontal Res. 2025 Jan;60(1):30-43. doi: 10.1111/jre.13324. Epub 2024 Jul 11. J Periodontal Res. 2025. PMID: 38991951 Review.
-
Gut dysbiosis induces the development of mastitis through a reduction in host anti-inflammatory enzyme activity by endotoxemia.Microbiome. 2022 Dec 1;10(1):205. doi: 10.1186/s40168-022-01402-z. Microbiome. 2022. PMID: 36451232 Free PMC article.
-
Oral Infections, Metabolic Inflammation, Genetics, and Cardiometabolic Diseases.J Dent Res. 2015 Sep;94(9 Suppl):119S-27S. doi: 10.1177/0022034515580795. Epub 2015 Apr 3. J Dent Res. 2015. PMID: 25840582 Review.
Cited by
-
Microbial functional pathways based on metatranscriptomic profiling enable effective saliva-based health assessments for precision wellness.Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2024 Jan 29;23:834-842. doi: 10.1016/j.csbj.2024.01.018. eCollection 2024 Dec. Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2024. PMID: 38328005 Free PMC article.
-
Periodontitis may predict the use of prescription medicines later in life, a database study.Front Pharmacol. 2023 Mar 13;14:1146475. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1146475. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 36992840 Free PMC article.
-
Association between lipid-A-producing oral bacteria of different potency and fractional exhaled nitric oxide in a Norwegian population-based adult cohort.J Transl Med. 2023 May 29;21(1):354. doi: 10.1186/s12967-023-04199-z. J Transl Med. 2023. PMID: 37246224 Free PMC article.
-
"Periodontal ligament-on-chip" as a Novel Tool for Studies on the Physiology and Pathology of Periodontal Tissues.Adv Healthc Mater. 2024 Dec;13(32):e2303942. doi: 10.1002/adhm.202303942. Epub 2024 Sep 16. Adv Healthc Mater. 2024. PMID: 39279543 Free PMC article.
-
Periodontal Therapy in Bariatric Surgery Patients with Periodontitis: Randomized Control Clinical Trial.J Clin Med. 2022 Nov 19;11(22):6837. doi: 10.3390/jcm11226837. J Clin Med. 2022. PMID: 36431314 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Rietschel ET, Kirikae T, Schade FU, et al. Bacterial endotoxin: molecular relationships of structure to activity and function. FASEB J. 1994;8:217‐225. - PubMed
-
- Cani PD, Amar J, Iglesias MA, et al. Metabolic endotoxemia initiates obesity and insulin resistance. Diabetes. 2007;56:1761‐1772. - PubMed
-
- Pradhan‐Palikhe P, Vikatmaa P, Lajunen T, et al. Elevated MMP‐8 and decreased myeloperoxidase concentrations associate significantly with the risk for peripheral atherosclerosis disease and abdominal aortic aneurysm. Scand J Immunol. 2010;72:150‐157. - PubMed
-
- Pussinen PJ, Tuomisto K, Jousilahti P, Havulinna AS, Sundvall J, Salomaa V. Endotoxemia, immune response to periodontal pathogens, and systemic inflammation associate with incident cardiovascular disease events. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2007;27:1433‐1439. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

