Model-based assessment of COVID-19 epidemic dynamics by wastewater analysis
- PMID: 35245552
- PMCID: PMC8886713
- DOI: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.154235
Model-based assessment of COVID-19 epidemic dynamics by wastewater analysis
Abstract
Continuous surveillance of COVID-19 diffusion remains crucial to control its diffusion and to anticipate infection waves. Detecting viral RNA load in wastewater samples has been suggested as an effective approach for epidemic monitoring and the development of an effective warning system. However, its quantitative link to the epidemic status and the stages of outbreak is still elusive. Modelling is thus crucial to address these challenges. In this study, we present a novel mechanistic model-based approach to reconstruct the complete epidemic dynamics from SARS-CoV-2 viral load in wastewater. Our approach integrates noisy wastewater data and daily case numbers into a dynamical epidemiological model. As demonstrated for various regions and sampling protocols, it quantifies the case numbers, provides epidemic indicators and accurately infers future epidemic trends. Following its quantitative analysis, we also provide recommendations for wastewater data standards and for their use as warning indicators against new infection waves. In situations of reduced testing capacity, our modelling approach can enhance the surveillance of wastewater for early epidemic prediction and robust and cost-effective real-time monitoring of local COVID-19 dynamics.
Keywords: COVID-19; Early warning system; Epidemiological modelling; Kalman filter; Surveillance of wastewater for early epidemic prediction (SWEEP); Wastewater-based epidemiology.
Copyright © 2022 The Authors. Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interest The authors declare the following financial interests/personal relationships which may be considered as potential competing interests: Atte Aalto reports financial support was provided by Luxembourg National Research Fund (FNR). Daniele Proverbio reports financial support was provided by Luxembourg National Research Fund (FNR). Francoise Kemp reports financial support was provided by Luxembourg National Research Fund (FNR). Stefano Magni reports financial support was provided by Luxembourg National Research Fund (FNR). Leslie Ogorzaly reports financial support was provided by Luxembourg National Research Fund (FNR). Henri-Michel Cauchie reports financial support was provided by Luxembourg National Research Fund (FNR). Jorge Goncalves reports financial support was provided by 111 Project on Computational Intelligence and Intelligent Control.
Figures
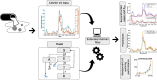
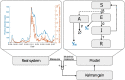
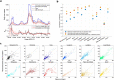




References
-
- Ahmed W., Bivins A., Simpson S.L., Bertsch P.M., Ehret J., Hosegood I., Metcalfe S., Smith W.J., Thomas K.V., Tynan J., et al. Wastewater surveillance demonstrates high predictive value for COVID-19 infection on board repatriation flights to Australia. Environ. Int. 2021;158 doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2021.106938. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

