HIV related stigma associated with social support, alcohol use disorders, depression, anxiety, and suicidal ideation among people living with HIV: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 35246211
- PMCID: PMC8896327
- DOI: 10.1186/s13033-022-00527-w
HIV related stigma associated with social support, alcohol use disorders, depression, anxiety, and suicidal ideation among people living with HIV: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: Stigma is a social phenomenon known to have a negative impact on the lives of people living with HIV (PLWH). However, defining HIV-related stigma (HRS) is difficult because of the intersection it has with structural inequalities, and cultural differences, discrimination by health care providers that measure stigma among PLWH. HIV/AIDS has been characterized as a traumatic experience and PLWH may experience stigma which can cause negative mental health disorders and experiences, including emotional distress, shame, depression, anxiety, suicidal ideation. A systematic review of the evidence on the mental disorders of PLWH is currently lacking. This study aimed to analyze the association between HRS and social support, alcohol use disorders and mental health disorders and experiences (depression, anxiety, and suicidal ideation) among PLWH.
Methods: In accordance with Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) this study searched PubMed, Scopus, Web of sciences, PsycInfo, SciELO and Cochrane library electronic databases to identify publications between January 1992 and August 2020 that discussed social support, alcohol use disorders, mental health disorders and experiences (i.e., depression and anxiety and suicidal ideation) associated with HRS. Pooled Odds Ratios (ORs) were utilized at a 95% confidence level, and as sampling methods differed between articles pooled estimates used a random effects model.
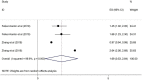
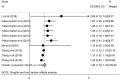
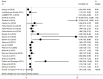
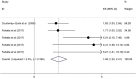
Results: Twenty-two studies with 9548 participants met the eligibility criteria. No association was observed between HRS and alcohol use disorders. PLWH who had higher levels of social supports were less likely to report HRS. Participants who had been diagnosed with anxiety were 1.89 times more likely to report HRS, while those diagnosed with depression were 1.61 times more. Respondents who reported suicidal ideation also were 1.83 times more likely to report HRS.
Conclusions: This meta-analysis supports that HRS has a detrimental association with anxiety, depression and suicidal ideation, but social support protects again HRS in PLWH. Applying interventions which focus on the mental health disorders of PLWH may decrease HRS. Provision of social support by practitioners, combined with mental health treatment and assessments, and designing methods to identify stigma at different stages of illness are warranted.
Keywords: Anxiety; Depression; Stigma; Suicidal ideation.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
A structural equation model of perceived and internalized stigma, depression, and suicidal status among people living with HIV/AIDS.BMC Public Health. 2018 Jan 15;18(1):138. doi: 10.1186/s12889-018-5053-1. BMC Public Health. 2018. PMID: 29334959 Free PMC article.
-
Socio-demographic, clinical and service use determinants associated with HIV related stigma among people living with HIV/AIDS: a systematic review and meta-analysis.BMC Health Serv Res. 2021 Sep 22;21(1):1004. doi: 10.1186/s12913-021-06980-6. BMC Health Serv Res. 2021. PMID: 34551772 Free PMC article.
-
Suicidal ideation of people living with HIV and its relations to depression, anxiety and social support.BMC Psychol. 2023 May 16;11(1):159. doi: 10.1186/s40359-023-01177-4. BMC Psychol. 2023. PMID: 37194090 Free PMC article.
-
Prevalence of Depression and Suicidal Ideation and Associated Risk Factors in Adolescents Receiving Care and Treatment for Hiv/Aids at a Tertiary Health Facility in Kilimanjaro Region, Tanzania.Res Sq [Preprint]. 2023 Feb 28:rs.3.rs-2534893. doi: 10.21203/rs.3.rs-2534893/v1. Res Sq. 2023. PMID: 36909487 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
Suicidal ideation and associated factors among people living with HIV/AIDS in Ethiopia: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Front Psychiatry. 2024 Sep 10;15:1361304. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2024.1361304. eCollection 2024. Front Psychiatry. 2024. PMID: 39319360 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Bifactor SEM and MIRT Structure of a 12-Item Human Immunodeficiency Virus Stigma Scale in Peruvian Adults.J Prim Care Community Health. 2023 Jan-Dec;14:21501319231197589. doi: 10.1177/21501319231197589. J Prim Care Community Health. 2023. PMID: 37750178 Free PMC article.
-
Prevalence of HIV-related stigma manifestations and their contributing factors among people living with HIV in Sweden - a nationwide study.BMC Public Health. 2024 May 20;24(1):1360. doi: 10.1186/s12889-024-18852-9. BMC Public Health. 2024. PMID: 38769531 Free PMC article.
-
Risk of suicide in people living with HIV: A nationwide, retrospective population-based cohort study in South Korea.J Int AIDS Soc. 2025 Jun;28(6):e26521. doi: 10.1002/jia2.26521. J Int AIDS Soc. 2025. PMID: 40474535 Free PMC article.
-
Prevalence of depression and associated factors among HIV/AIDS patients attending antiretroviral therapy clinic at Adama Hospital Medical College, Adama, Central Ethiopia.Sci Rep. 2024 Jan 18;14(1):1642. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-52142-z. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38238489 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluating knowledge about HIV and discriminatory attitudes among Pakistani women of reproductive age using 2017-18 Demographic Health Survey data.Sci Rep. 2023 Oct 19;13(1):17849. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-45117-z. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37857793 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Logie C, Gadalla TM. Meta-analysis of health and demographic correlates of stigma towards people living with HIV. AIDS Care. 2009;21(6):742–753. - PubMed
-
- Thomas BE, Rehman F, Suryanarayanan D, Josephine K, Dilip M, Dorairaj VS, Swaminathan S. How stigmatizing is stigma in the life of people living with HIV: a study on HIV positive individuals from Chennai, South India. AIDS Care. 2005;17(7):795–801. - PubMed
-
- Heckman TG, Heckman BD, Kochman A, Sikkema KJ, Suhr J, Goodkin K. Psychological symptoms among persons 50 years of age and older living with HIV disease. Aging Ment Health. 2002;6(2):121–128. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

