The Critical and Diverse Roles of CD4-CD8- Double Negative T Cells in Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease
- PMID: 35247631
- PMCID: PMC9059101
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jcmgh.2022.02.019
The Critical and Diverse Roles of CD4-CD8- Double Negative T Cells in Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease
Abstract
Background & aims: Hepatic inflammation is a hallmark of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). Double negative T (DNT) cells are a unique subset of T lymphocytes that do not express CD4, CD8, or natural killer cell markers, and studies have suggested that DNT cells play critical and diverse roles in the immune system. However, the role of intrahepatic DNT cells in NAFLD is largely unknown.
Methods: The proportions and RNA transcription profiling of intrahepatic DNT cells were compared between C57BL/6 mice fed with control diet or methionine-choline-deficient diet for 5 weeks. The functions of DNT cells were tested in vitro and in vivo.
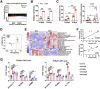
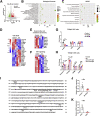
Results: The proportion of intrahepatic DNT cells was significantly increased in mice with diet-induced NAFLD. In NAFLD mice, the proportion of intrahepatic TCRγδ+ DNT cells was increased along with elevated interleukin (IL) 17A; in contrast, the percentage of TCRαβ+ DNT cells was decreased, accompanied by reduced granzyme B (GZMB). TCRγδ+ DNT cell depletion resulted in lowered liver IL17A levels and significantly alleviated NAFLD. Adoptive transfer of intrahepatic TCRαβ+ DNT cells from control mice increased intrahepatic CD4 and CD8 T cell apoptosis and inhibited NAFLD progression. Furthermore, we revealed that adrenic acid and arachidonic acid, harmful fatty acids that were enriched in the liver of the mice with NAFLD, could induce apoptosis of TCRαβ+ DNT cells and inhibit their immunosuppressive function and nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB) or AKT signaling pathway activity. However, arachidonic acid facilitated IL17A secretion by TCRγδ+ DNT cells, and the NF-κB signaling pathway was involved. Finally, we also confirmed the variation of intrahepatic TCRαβ+ DNT cells and TCRγδ+ DNT cells in humans.
Conclusions: During NAFLD progression, TCRγδ+ DNT cells enhance IL17A secretion and aggravate liver inflammation, whereas TCRαβ+ DNT cells decrease GZMB production and lead to weakened immunoregulatory function. Shifting of balance from TCRγδ+ DNT cell response to one that favors TCRαβ+ DNT regulation would be beneficial for the prevention and treatment of NAFLD.
Keywords: GZMB; IL17A; NAFLD; TCRαβ(+) DNT Cells; TCRγδ(+) DNT Cells.
Copyright © 2022 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures










Similar articles
-
Distinct Features of Canine Non-conventional CD4-CD8α- Double-Negative TCRαβ+ vs. TCRγδ+ T Cells.Front Immunol. 2019 Nov 22;10:2748. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.02748. eCollection 2019. Front Immunol. 2019. PMID: 31824515 Free PMC article.
-
TCRγδ(+)CD4(-)CD8(-) T cells suppress the CD8(+) T-cell response to hepatitis B virus peptides, and are associated with viral control in chronic hepatitis B.PLoS One. 2014 Feb 14;9(2):e88475. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0088475. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24551107 Free PMC article.
-
The immunoregulatory effects of CD8 T-cell-derived perforin on diet-induced nonalcoholic steatohepatitis.FASEB J. 2019 Jul;33(7):8490-8503. doi: 10.1096/fj.201802534RR. Epub 2019 Apr 5. FASEB J. 2019. PMID: 30951375
-
Alleviation of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease by Huazhi Fugan Granules is associated with suppression of TLR4/NF-κB signaling pathway.Clin Investig Arterioscler. 2021 Sep-Oct;33(5):257-266. doi: 10.1016/j.arteri.2020.12.007. Epub 2021 Mar 31. Clin Investig Arterioscler. 2021. PMID: 33810882 Review. English, Spanish.
-
Regulatory Networks, Management Approaches, and Emerging Treatments of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease.Can J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2022 Nov 8;2022:6799414. doi: 10.1155/2022/6799414. eCollection 2022. Can J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2022. PMID: 36397950 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Testing Green Tea Extract and Ammonium Salts as Stimulants of Physical Performance in a Forced Swimming Rat Experimental Model.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Sep 27;25(19):10438. doi: 10.3390/ijms251910438. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39408765 Free PMC article.
-
The immunology of sickness metabolism.Cell Mol Immunol. 2024 Sep;21(9):1051-1065. doi: 10.1038/s41423-024-01192-4. Epub 2024 Aug 6. Cell Mol Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39107476 Free PMC article. Review.
-
TCRαβ+NK1.1-CD4-CD8- double-negative T cells inhibit central and peripheral inflammation and ameliorate ischemic stroke in mice.Theranostics. 2023 Jan 10;13(3):896-909. doi: 10.7150/thno.80307. eCollection 2023. Theranostics. 2023. PMID: 36793857 Free PMC article.
-
Salidroside may target PPARα to exert preventive and therapeutic activities on NASH.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Oct 2;15:1433076. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1433076. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39415834 Free PMC article.
-
Adrenic acid: A promising biomarker and therapeutic target (Review).Int J Mol Med. 2025 Feb;55(2):20. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2024.5461. Epub 2024 Nov 22. Int J Mol Med. 2025. PMID: 39575474 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Younossi Z., Anstee Q.M., Marietti M., Hardy T., Henry L., Eslam M., George J., Bugianesi E. Global burden of NAFLD and NASH: trends, predictions, risk factors and prevention. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2018;15:11–20. - PubMed
-
- Petroni M.L., Brodosi L., Bugianesi E., Marchesini G. Management of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. BMJ. 2021;372 - PubMed
-
- Sheka A.C., Adeyi O., Thompson J., Hameed B., Crawford P.A., Ikramuddin S. Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: a review. JAMA. 2020;323:1175–1183. - PubMed
-
- Cai J., Zhang X.J., Li H. The role of innate immune cells in nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Hepatology. 2019;70:1026–1037. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

