DFNA5 regulates immune cells infiltration and exhaustion
- PMID: 35248047
- PMCID: PMC8897971
- DOI: 10.1186/s12935-022-02487-0
DFNA5 regulates immune cells infiltration and exhaustion
Abstract
Background: DFNA5 (GSDME) belongs to Gasdermin familily that is involved in a variety of cancers and triggers cell pyroptosis after chemical treatment. However, the relationship in DFNA5 between prognosis and immune cells in diverse cancers has been receiving little attention. Tumor immune cells infiltration and exhaustion may associate with patients prognosis. The roles of DFNA5 in tumor immune cells infiltration and exhaustion have not been clarified.
Methods: The expression level of DFNA5 was determined by the Tumour Immune Estimation Resource and the Oncomine database. Then the impacts of DFNA5 in prognosis were assessed by Kaplan-Meier plotter and ULACAN. The correlations between DFNA5 and tumour-infiltrating lymphocytes were explored by TIMER. In addition, the relationships in the expression levels of DFNA5 and typical genes combination of tumour-infiltrating lymphocytes were analysed by GEPIA and TIMER. In this study, we screened the chemokine and immune related proteins interacted with DFNA5 using TurboID system to explore the instantaneous or weak interactions.
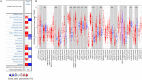
Results: DFNA5 significantly influences the prognosis in different cancers according to The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA). The expression levels of DFNA5 showed positive correlations to the infiltration of macrophages, CD8 + T cells, CD4 + T cells in liver hepatocellular carcinoma (LIHC), colon adenocarcinoma (COAD), and lung adenocarcinoma (LUAD). DFNA5 expression displayed obvious correlations with multiple lymphocytes gene makers in COAD, LIHC and LUAD. DFNA5 expression has effects on the prognosis of liver hepatocellular carcinoma and LUAD. DFNA5 upregulated the expression levels of PDCD1 and CD274 in a dose-dependent manner. Chemokine and immune related proteins interact with DFNA5.
Conclusions: These results indicate that DFNA5 is related to patient prognosis and immune cells, consisting of macrophages, CD4 + T cells, and CD8 + T cells, in diverse cancers. In addition, DFNA5 expression might contribute to the regulation of T cell exhaustion, tumour-associated macrophages (TAMs), and Tregs in COAD, LIHC and LUAD. DFNA5 may regulate immune infiltration via EIF2AK2. IFNGR1 was related to the functions of PD-L1 expression and PD-1 checkpoint pathway. These results indicate that DFNA5 levels may be act as a prognostic factor and predict the degrees of immune cells infiltration in LIHC and LUAD.
Keywords: CD274; Cancer; DFNA5; Prognosis; Tumour-infiltrating lymphocytes.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures




References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

