Hospitalization for computer-assisted hexapod ring fixation application - analyses of patient variability, peri-operative complications, hospital costs, and discharge status
- PMID: 35248052
- PMCID: PMC8897910
- DOI: 10.1186/s12891-022-05171-6
Hospitalization for computer-assisted hexapod ring fixation application - analyses of patient variability, peri-operative complications, hospital costs, and discharge status
Abstract
Background: Computer-assisted hexapod ring fixation systems (HRF) are used for multiple conditions and in very diverse patient populations. This study analyzes perioperative outcomes following HRF application based on patient etiology and clinical presentation.
Methods: Data from patients in the Premier Hospital Billing Database between 2007-2019 undergoing HRF application were analyzed for the duration of patients' hospitalizations. Patients were grouped based on etiology: acquired deformity, arthrosis, congenital deformity, deep infection, infected nonunion, fracture, nonunion, and other post-operative complications. Demographics, comorbidities, operating room time (ORT), length of stay (LOS), peri-operative complications, and hospital costs were estimated using generalized linear models. Logistic regression evaluated factors associated with peri-operative complications.
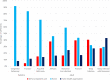
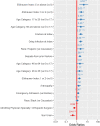
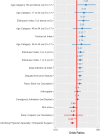
Results: One thousand eight hundred eighteen patients (average age: 46.9, standard deviation (SD) (19.6) - 38.9% female) were included in the study, and included 72% fracture cases, 9.6% deep infection, 10.2% deformity (acquired: 5.9%, congenital: 4.3%), 4.2% nonunions, 2% arthrosis and 1.4% other sequelas from prior fractures. Comorbidities varied across diagnosis categories and age, 40% adults and 86% pediatric had no comorbidities. Pediatric cases mostly suffered from obesity (16.1%) and pulmonary disease (10.7%). Complicated diabetes was present in 45.9% of arthropathy and 34.3% of deep infection patients. ORT, LOS and inflation-adjusted hospital costs for all patients averaged 277.7 min (95% Confidence interval (CI): 265.1-290.3), 7.07 days (95% CI: 6.6-7.5) and $41,507 (95%CI: $39,728-$43,285), respectively, but were highest in patients with deep infection (ORT: 369 min (95%CI: $321.0-$433.8); LOS: 14.4 days (95%CI: $13.7-$15.1); Cost: $54,666 (95%CI: $47,960-$63,553)). The probability of having an intraoperative complication averaged 35% (95%CI: 28%-43%) in adult patients with deep infection vs 7% (95%CI: 2%-20%) in pediatric cases treated for congenital deformity. The risk for intraoperative complications was mostly associated with preexisting comorbidities, an Elixhauser > 5 was the most predictive risk factor for complications (odds ratios: 4.53 (95%CI: 1.71-12.00, p = 0.002).
Conclusions: There is important heterogeneity among HRF patients. Adults with HRF for fracture, deep infection and arthrosis are at far greater risk for peri-operative complications vs. patients with deformity, especially pediatric deformity cases, mostly due to existing comorbidities and age. Device-specific HRF clinical studies cannot be generalized beyond their exact patient population.
Keywords: Complications; Costs; Hexapod ring fixation; Hospital; Long bone deformities; Resource utilization.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
MV, AC, CEH, and CS are employees of Johnson & Johnson (JnJ) and own stock in the company. BR was a contractor with JnJ at the time of the study. JSR is a consultant for JnJ but holds no stock nor receives royalty payments.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Two-year clinical and economic burden, risk and outcomes following application of software-assisted hexapod ring fixation systems.BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2022 Jan 3;23(1):25. doi: 10.1186/s12891-021-04934-x. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2022. PMID: 34980051 Free PMC article.
-
The Frank Stinchfield Award : Total Hip Arthroplasty for Femoral Neck Fracture Is Not a Typical DRG 470: A Propensity-matched Cohort Study.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2017 Feb;475(2):353-360. doi: 10.1007/s11999-016-4868-2. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2017. PMID: 27154530 Free PMC article.
-
Factors affecting length of stay after elective posterior lumbar spine surgery: a multivariate analysis.Spine J. 2015 Jun 1;15(6):1188-95. doi: 10.1016/j.spinee.2013.10.022. Epub 2013 Nov 1. Spine J. 2015. PMID: 24184639
-
Impact of associated injuries in conjunction with fracture of the axis vertebra on inpatient outcomes and postoperative complications: a Nationwide Inpatient Sample analysis from 2002 to 2011.Spine J. 2016 Apr;16(4):491-503. doi: 10.1016/j.spinee.2015.12.006. Epub 2015 Dec 14. Spine J. 2016. PMID: 26698655
-
Factors associated with hospital stay length, discharge destination, and 30-day readmission rate after primary hip or knee arthroplasty: Retrospective Cohort Study.Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2019 Sep;105(5):949-955. doi: 10.1016/j.otsr.2019.04.012. Epub 2019 Jun 15. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2019. PMID: 31208932 Review.
Cited by
-
Definition of a measurement technique for hexapod circular smart fixators' perioperative assembly parameters and investigation of alignment and correlation with postoperative measurements: a retrospective cohort study.BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2024 Nov 20;25(1):933. doi: 10.1186/s12891-024-08056-y. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2024. PMID: 39563261 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Tsibidakis H, Kanellopoulos AD, Sakellariou VI, Soultanis K, Zoubos AB, Soucacos PN. The role of Taylor Spatial Frame for the treatment of acquired and congenital tibial deformities in children. Acta Orthop Belg. 2014;80(3):419–425. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

