The application of mass spectrometry imaging in traditional Chinese medicine: a review
- PMID: 35248086
- PMCID: PMC8898510
- DOI: 10.1186/s13020-022-00586-8
The application of mass spectrometry imaging in traditional Chinese medicine: a review
Abstract
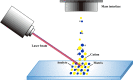
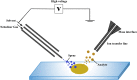
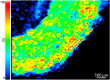
Mass spectrometry imaging is a frontier technique which connects classical mass spectrometry with ion imaging. Various types of chemicals could be visualized in their native tissues using mass spectrometry imaging. Up to now, the most commonly applied mass spectrometry imaging techniques are matrix assisted laser desorption ionization mass spectrometry imaging, desorption electrospray ionization mass spectrometry imaging and secondary ion mass spectrometry imaging. This review gives an introduction to the principles, development and applications of commonly applied mass spectrometry imaging techniques, and then illustrates the application of mass spectrometry imaging in the investigation of traditional Chinese medicine. Recently, mass spectrometry imaging has been adopted to explore the spatial distribution of endogenous metabolites in traditional Chinese medicine. Data collected from mass spectrometry imaging can be further utilized to search for marker components of traditional Chinese medicine, discover new compounds from traditional herbs, and differentiate between medicinal plants that are similar in botanical features. Moreover, mass spectrometry imaging also plays a role in revealing the pharmacological and toxicological mechanisms of traditional Chinese medicine.
Keywords: Mass spectrometry imaging; Medicinal plants; Natural compounds; Spatial distribution; Traditional Chinese medicine.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Localization of ginsenosides in Panax ginseng with different age by matrix-assisted laser-desorption/ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry imaging.J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2016 Jul 15;1026:263-271. doi: 10.1016/j.jchromb.2015.09.024. Epub 2015 Oct 23. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2016. PMID: 26520809
-
Visualization of Metabolites Identified in the Spatial Metabolome of Traditional Chinese Medicine Using DESI-MSI.J Vis Exp. 2022 Dec 16;(190). doi: 10.3791/64912. J Vis Exp. 2022. PMID: 36591997
-
[Application of MALDI-mass spectrometry imaging in spatial distribution of secondary metabolites in medicinal plants -- a case study of Lepdium meyenii root].Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2020 Feb;45(3):596-601. doi: 10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.20191209.201. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2020. PMID: 32237518 Chinese.
-
Surface analysis of lipids by mass spectrometry: more than just imaging.Prog Lipid Res. 2013 Oct;52(4):329-53. doi: 10.1016/j.plipres.2013.04.005. Epub 2013 Apr 24. Prog Lipid Res. 2013. PMID: 23623802 Review.
-
Use of mass spectrometry for imaging metabolites in plants.Plant J. 2012 Apr;70(1):81-95. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-313X.2012.04899.x. Plant J. 2012. PMID: 22449044 Review.
Cited by
-
Spatial Metabolomics and Its Application in Plant Research.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Mar 26;26(7):3043. doi: 10.3390/ijms26073043. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40243661 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Revealing the Preventable Effects of Fu-Zheng-Qu-Xie Decoction against Recurrence and Metastasis of Postoperative Early-Stage Lung Adenocarcinoma Based on Network Pharmacology Coupled with Metabolomics Analysis.ACS Omega. 2023 Sep 20;8(39):35555-35570. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.3c00122. eCollection 2023 Oct 3. ACS Omega. 2023. PMID: 37810735 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of ginsenosides from Panax japonicus var. major (Zhu-Zi-Shen) based on ultra-high performance liquid chromatography/quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry and desorption electrospray ionization-mass spectrometry imaging.Chin Med. 2023 Sep 8;18(1):115. doi: 10.1186/s13020-023-00830-9. Chin Med. 2023. PMID: 37684699 Free PMC article.
-
Application of multi-omics in the study of traditional Chinese medicine.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Sep 6;15:1431862. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1431862. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39309011 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometry imaging analysis revealed the spatial distribution of metabolites during Ziziphi Spinosae Semen at different growth periods.Front Plant Sci. 2025 Feb 21;16:1510310. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2025.1510310. eCollection 2025. Front Plant Sci. 2025. PMID: 40061039 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Liu X, Wu W, Jiang B, Yang M, Guo D. Pharmacological tools for the development of traditional Chinese medicine. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2013;34:620–628. - PubMed
-
- Jin H, Liu Y, Guo Z, Wang J, Zhang X, Wang C, et al. Recent development in liquid chromatography stationary phases for separation of Traditional Chinese Medicine components. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2016;130:336–346. - PubMed
-
- Ruan C, Xu G, Lu X, Hua R, Kong H, Xiao K, et al. Quality evaluation of volatile oils of traditional Chinese medicines by using comprehensive two-dimensional gas chromatography (GC x GC) Chromatographia. 2005;57:265–270.
-
- Chen Y, Xie MY, Wang YX, Nie SP, Li C. Analysis of the monosaccharide composition of purified polysaccharides in Ganoderma atrum by capillary gas chromatography. Phytochem Anal. 2009;20:503–510. - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

