Prevalence of human papilloma virus (HPV) genotypes between outpatients males and females referred to seven laboratories in Tehran, Iran
- PMID: 35248145
- PMCID: PMC8897875
- DOI: 10.1186/s13027-022-00421-7
Prevalence of human papilloma virus (HPV) genotypes between outpatients males and females referred to seven laboratories in Tehran, Iran
Abstract
Background: Human papilloma virus (HPV) causes the most common sexually-transmitted infection especially among sexually-active individuals. The aim of study was to characterize the molecular characterization of HPV genotypes between 5176 female and male patients.
Methods: HPV DNA was extracted from genital swabs of the study participants and amplified by Real Time Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR). Genotyping was performed for 2525 cases using REALQUALITY RQ-Multi HPV Detection Kit for the identification of 14 high risk (HR) and 2 low risk (LR) HPV genotypes. Demographic figures were analyzed in correlation with virological data statistically.
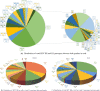
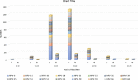
Results: Out of 5176 cases from 7 laboratories, 2727 (53%) were positive for HPV, of which. 2372(87%) women and 355 (13%) men were HPV positive. However, in an intra-gender analysis, positive rate was higher in men (355/637, 55.7%) than in women (2372/4539, 52%; P value 0.007). HPV positive patients were younger than negative individuals. Positive rate was higher among age categories 20-40. Genotyping was performed for 2525 cases. Out of 1219 (48%) patients who contained single genotypes, 566 (22%) and 653 (26%) harboured HR and LR genotypes, respectively. In females and males, 1189 (54%) and 117 (37%) contained multiple genotypes. No substantial associations were found between different age categories and HR/LR and multiple genotypes distribution.
Conclusion: The prevalence of HPV infection in both genders was high. However, men had a higher rate of infection. These observations highlighted the necessity for a plan for targeted education to younger population in the society as well as application of infection control measures against HPV infection, especially in terms of general population mass HPV vaccination.
Keywords: Cervical cancer; Human papilloma virus; Sexually-transmitted infections.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Uncommon high distribution of HPV-16, HPV-54, and HPV-56 in female referred to a laboratory in Karaj, Iran: indications of a paradigm shift in HPV genotypes?Virol J. 2024 Aug 9;21(1):182. doi: 10.1186/s12985-024-02457-0. Virol J. 2024. PMID: 39123176 Free PMC article.
-
Prevalence of high and low risk HPV genotypes among vaccinated and non-vaccinated people in Tehran.Virol J. 2024 Jan 5;21(1):9. doi: 10.1186/s12985-023-02270-1. Virol J. 2024. PMID: 38183101 Free PMC article.
-
Prevalence and genotype distribution of human papillomavirus in individuals referred to a laboratory in Urmia, Iran.Infect Agent Cancer. 2025 Mar 3;20(1):13. doi: 10.1186/s13027-025-00636-4. Infect Agent Cancer. 2025. PMID: 40033426 Free PMC article.
-
The Association of High Risk Human Papillomaviruses in Patients With Cervical Cancer: An Evidence Based Study on Patients With Squamous Cell Dysplasia or Carcinoma for Evaluation of 23 Human Papilloma Virus Genotypes.Jundishapur J Microbiol. 2016 Feb 17;9(4):e32728. doi: 10.5812/jjm.32728. eCollection 2016 Apr. Jundishapur J Microbiol. 2016. PMID: 27279992 Free PMC article.
-
Annual disease burden due to human papillomavirus (HPV) 6 and 11 infections in Finland.Scand J Infect Dis Suppl. 2009;107:3-32. doi: 10.1080/00365540902887730. Scand J Infect Dis Suppl. 2009. PMID: 19408160 Review.
Cited by
-
Prevailing of HPV-16 and 52 genotype in 2022-2023 in Sanandaj, Iran.Virol J. 2024 May 7;21(1):106. doi: 10.1186/s12985-024-02373-3. Virol J. 2024. PMID: 38715018 Free PMC article.
-
PATHOMORPHOLOGY OF VERRUCAE: A CLINICOPATHOLOGIC STUDY.Ann Ib Postgrad Med. 2024 Dec 31;22(3):84-89. Ann Ib Postgrad Med. 2024. PMID: 40385707 Free PMC article.
-
Prevalence of human papillomavirus (HPV) genotypes in patients with clinical symptoms in Kermanshah, western Iran: a cross-sectional study.BMC Infect Dis. 2025 Feb 16;25(1):226. doi: 10.1186/s12879-025-10563-9. BMC Infect Dis. 2025. PMID: 39956900 Free PMC article.
-
Prevalence and genotype distribution of HPV infection among women in 2021-2023 in southern Iran: The rising trend of HPV infection among women.BMC Womens Health. 2025 Mar 20;25(1):126. doi: 10.1186/s12905-025-03668-5. BMC Womens Health. 2025. PMID: 40114128 Free PMC article.
-
Uncommon high distribution of HPV-16, HPV-54, and HPV-56 in female referred to a laboratory in Karaj, Iran: indications of a paradigm shift in HPV genotypes?Virol J. 2024 Aug 9;21(1):182. doi: 10.1186/s12985-024-02457-0. Virol J. 2024. PMID: 39123176 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

