The RNA-binding protein HuR in human cancer: A friend or foe?
- PMID: 35248670
- PMCID: PMC9035123
- DOI: 10.1016/j.addr.2022.114179
The RNA-binding protein HuR in human cancer: A friend or foe?
Abstract
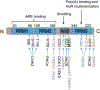
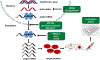
The RNA-binding proteins (RBPs) are critical trans factors that associate with specific cis elements present in mRNAs whose stability and translation are subject to regulation. The RBP Hu antigen R (HuR) is overexpressed in a wide variety of human cancers and serves as a prognostic factor of poor clinical outcome. HuR promotes tumorigenesis by interacting with a subset of oncogenic mRNAs implicated in different cancer hallmarks, and resistance to therapy. Reduction of HuR levels in cancer cells leads to tumor regression in mouse xenograft models. These findings prompt a working model whereby cancer cells use HuR, a master switch of multiple oncogenic mRNAs, to drive drug resistance and promote cell survival and metastasis, thus rendering the tumor cells with high cytoplasmic HuR more progressive and resistant to therapy. This review summarizes the roles of HuR in cancer and other diseases, therapeutic potential of HuR inhibition, and the current status of drug discovery on HuR.
Keywords: Cancer; Companion assay; Drug development; Drug discovery; Drug resistance; HuR; Molecular therapy; RNA-binding protein; Small molecules.
Copyright © 2022 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Competing Interest The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Identification of tumorigenesis-related mRNAs associated with RNA-binding protein HuR in thyroid cancer cells.Oncotarget. 2016 Sep 27;7(39):63388-63407. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.11255. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27542231 Free PMC article.
-
An RNA-Binding Protein, Hu-antigen R, in Pancreatic Cancer Epithelial to Mesenchymal Transition, Metastasis, and Cancer Stem Cells.Mol Cancer Ther. 2020 Nov;19(11):2267-2277. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-19-0822. Epub 2020 Sep 2. Mol Cancer Ther. 2020. PMID: 32879054 Free PMC article.
-
Identification and validation of novel small molecule disruptors of HuR-mRNA interaction.ACS Chem Biol. 2015 Jun 19;10(6):1476-84. doi: 10.1021/cb500851u. Epub 2015 Mar 17. ACS Chem Biol. 2015. PMID: 25750985 Free PMC article.
-
HuR as a molecular target for cancer therapeutics and immune-related disorders.Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2022 Sep;188:114442. doi: 10.1016/j.addr.2022.114442. Epub 2022 Jul 8. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2022. PMID: 35817212 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Understanding and targeting the disease-related RNA binding protein human antigen R (HuR).Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2020 May;11(3):e1581. doi: 10.1002/wrna.1581. Epub 2020 Jan 23. Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2020. PMID: 31970930 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Rationally designed inhibitors of the Musashi protein-RNA interaction by hotspot mimicry.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 Jan 10:2023.01.09.523326. doi: 10.1101/2023.01.09.523326. bioRxiv. 2023. PMID: 36711508 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
Mechanistic insights into the role of EGLN3 in pulmonary vascular remodeling and endothelial dysfunction.Respir Res. 2025 Feb 21;26(1):61. doi: 10.1186/s12931-025-03144-6. Respir Res. 2025. PMID: 39985019 Free PMC article. Review.
-
RBMS3-loss impedes TRIM21-induced ubiquitination of ANGPT2 in an RNA-independent manner and drives sorafenib resistance in hepatocellular carcinoma.Oncogene. 2025 Jun;44(21):1620-1633. doi: 10.1038/s41388-025-03335-x. Epub 2025 Mar 11. Oncogene. 2025. PMID: 40069332
-
Deciphering the multifaceted role of circular RNA in aging: from molecular mechanisms to therapeutic potentials.Noncoding RNA Res. 2025 May 30;14:129-144. doi: 10.1016/j.ncrna.2025.05.015. eCollection 2025 Oct. Noncoding RNA Res. 2025. PMID: 40585063 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nuclear receptor coactive 4-mediated ferritinophagy: a key role of heavy metals toxicity.Arch Toxicol. 2025 Apr;99(4):1257-1270. doi: 10.1007/s00204-025-03963-y. Epub 2025 Feb 10. Arch Toxicol. 2025. PMID: 39928088 Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

