Purinergic P2X7 receptor antagonist ameliorates intestinal inflammation in postoperative ileus
- PMID: 35249909
- PMCID: PMC9096048
- DOI: 10.1292/jvms.22-0014
Purinergic P2X7 receptor antagonist ameliorates intestinal inflammation in postoperative ileus
Abstract
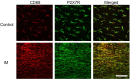
Postoperative ileus (POI) is a postsurgical gastrointestinal motility dysfunction caused by mechanical stress to the intestine during abdominal surgery. POI leads to nausea and vomiting reduced patient quality of life, as well as high medical costs and extended hospitalization. Intestinal inflammation caused by macrophages and neutrophils is thought to be important in the mechanism of POI. Surgery-associated tissue injury and inflammation induce the release of adenosine triphosphate (ATP) from injured cells. Released ATP binds the purinergic P2X7 receptor (P2X7R) expressed on inflammatory cells, inducing the secretion of inflammatory mediators. P2X7R antagonists are thought to be important mediators of the first step in the inflammation process, and studies in chemically induced colitis models confirmed that P2X7R antagonists exhibit anti-inflammatory effects. Therefore, we hypothesized that P2X7R plays an important role in POI. POI models were generated from C57BL/6J mice. Mice were treated with P2X7R antagonist A438079 (34 mg/kg) 30 min before and 2 hr after intestinal manipulation (IM). Inflammatory cell infiltration and gastrointestinal transit were measured. A438079 ameliorated macrophage and neutrophil infiltration in the POI model. Impaired intestinal transit improved following A438079 treatment. P2X7R was expressed on both infiltrating and resident macrophages in the inflamed ileal muscle layer. The P2X7R antagonist A438079 exhibits anti-inflammatory effects via P2X7R expressed on macrophages and therefore could be a target in the treatment of POI.
Keywords: P2X7 receptor; anti-inflammation; macrophages; postoperative ileus.
Figures