Efficacy and safety of low-dose interleukin-2 in combination with methotrexate in patients with active rheumatoid arthritis: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase 2 trial
- PMID: 35250032
- PMCID: PMC8898945
- DOI: 10.1038/s41392-022-00887-2
Efficacy and safety of low-dose interleukin-2 in combination with methotrexate in patients with active rheumatoid arthritis: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase 2 trial
Abstract
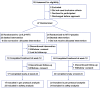
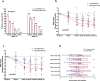
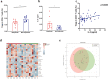
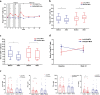
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is an aggressive autoimmune arthritis, and current therapies remain unsatisfactory due to low remission rate and substantially adverse effects. Low-dose interleukin-2 (Ld-IL2) is potentially a therapeutic approach to further improve the disease. This randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial was undertaken to evaluate the efficacy and safety of Ld-IL2 in patients with active RA. Patients were randomly assigned (1:1) to receive Ld-IL2, defined as a dose of 1 million IU, or placebo in a 12-week trial with a 12-week follow-up. Three cycles of Ld-IL2 or placebo were administered subcutaneously every other day for 2 weeks (a total of 7 doses), followed by a 2-week break. All patients received a stable dose of methotrexate (MTX). The primary outcomes were the proportion of patients achieving the ACR20, DAS28-ESR <2.6, and the change from baseline in CDAI or SDAI at week 24. Secondary endpoints included other clinical responses and safety. The primary outcomes were achieved in the per-protocol population. The improvements from baseline in CDAI and SDAI were significantly greater across time points for the Ld-IL2 + MTX group (n = 17) than for the placebo+MTX group (n = 23) (P = 0.018 and P = 0.015, respectively). More patients achieved ACR20 response in the Ld-IL2 + MTX group than those in the placebo+MTX group at week 12 (70.6% vs 43.5%) and at week 24 (76.5% vs 56.5%) (P = 0.014). In addition, low Treg and high IL-21 were associated with good responses to Ld-IL2. Ld-IL-2 treatment was well-tolerated in this study. These results suggested that Ld-IL2 was effective and safe in RA. ClinicalTrials.gov number: NCT02467504.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
We have no conflicts of interest. The sponsor was not involved with the collection, management, analysis, interpretation of the data, or preparation of the manuscript. The corresponding authors had full access to all the data in the study and had the final responsibility for the decision to submit the paper.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

