IgG Binds Escherichia coli Serine Protease EspP and Protects Mice From E. coli O157:H7 Infection
- PMID: 35250980
- PMCID: PMC8894809
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.807959
IgG Binds Escherichia coli Serine Protease EspP and Protects Mice From E. coli O157:H7 Infection
Abstract
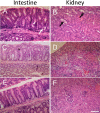
Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli O157:H7 is a virulent strain causing severe gastrointestinal infection, hemolytic uremic syndrome and death. To date there are no specific therapies to reduce progression of disease. Here we investigated the effect of pooled immunoglobulins (IgG) on the course of disease in a mouse model of intragastric E. coli O157:H7 inoculation. Intraperitoneal administration of murine IgG on day 3, or both on day 3 and 6, post-inoculation improved survival and decreased intestinal and renal pathology. When given on both day 3 and 6 post-inoculation IgG treatment also improved kidney function in infected mice. Murine and human commercially available IgG preparations bound to proteins in culture filtrates from E. coli O157:H7. Bound proteins were extracted from membranes and peptide sequences were identified by mass spectrometry. The findings showed that murine and human IgG bound to E. coli extracellular serine protease P (EspP) in the culture filtrate, via the IgG Fc domain. These results were confirmed using purified recombinant EspP and comparing culture filtrates from the wild-type E. coli O157:H7 strain to a deletion mutant lacking espP. Culture filtrates from wild-type E. coli O157:H7 exhibited enzymatic activity, specifically associated with the presence of EspP and demonstrated as pepsin cleavage, which was reduced in the presence of murine and human IgG. EspP is a virulence factor previously shown to promote colonic cell injury and the uptake of Shiga toxin by intestinal cells. The results presented here suggest that IgG binds to EspP, blocks its enzymatic activity, and protects the host from E. coli O157:H7 infection, even when given post-inoculation.
Keywords: Escherichia coli O157:H7; EspP; Shiga toxin; hemolytic uremic syndrome; immunoglobulin G; mouse.
Copyright © 2022 Tontanahal, Sperandio, Kovbasnjuk, Loos, Kristoffersson, Karpman and Arvidsson.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Overexpressed Proteins in Hypervirulent Clade 8 and Clade 6 Strains of Escherichia coli O157:H7 Compared to E. coli O157:H7 EDL933 Clade 3 Strain.PLoS One. 2016 Nov 23;11(11):e0166883. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0166883. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27880834 Free PMC article.
-
Subtypes of the plasmid-encoded serine protease EspP in Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli: distribution, secretion, and proteolytic activity.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2007 Oct;73(20):6351-9. doi: 10.1128/AEM.00920-07. Epub 2007 Aug 17. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2007. PMID: 17704265 Free PMC article.
-
EspP, an Extracellular Serine Protease from Enterohemorrhagic E. coli, Reduces Coagulation Factor Activities, Reduces Clot Strength, and Promotes Clot Lysis.PLoS One. 2016 Mar 2;11(3):e0149830. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0149830. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 26934472 Free PMC article.
-
Hemolytic uremic syndrome associated with Escherichia coli O157:H7 infection in older adults: a case report and review of the literature.J Med Case Rep. 2016 Jun 15;10:175. doi: 10.1186/s13256-016-0970-z. J Med Case Rep. 2016. PMID: 27301547 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Serine proteases autotransporter of Enterobacteriaceae: Structures, subdomains, motifs, functions, and targets.Mol Microbiol. 2023 Aug;120(2):178-193. doi: 10.1111/mmi.15116. Epub 2023 Jul 1. Mol Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 37392318 Review.
Cited by
-
Drug resistance and pathogenicity characteristics of Escherichia coli causing pneumonia in farmed foxes.Front Vet Sci. 2025 Apr 9;12:1567009. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2025.1567009. eCollection 2025. Front Vet Sci. 2025. PMID: 40271487 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of Single and Multi-Strain Probiotics with Gentamicin Against E. coli O157:H7: Insights from In Vitro and In Vivo Studies.Microorganisms. 2025 Feb 19;13(2):460. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms13020460. Microorganisms. 2025. PMID: 40005825 Free PMC article.
-
Outcomes from the International Society of Nephrology Hemolytic Uremic Syndromes International Forum.Kidney Int. 2024 Dec;106(6):1038-1050. doi: 10.1016/j.kint.2024.09.012. Epub 2024 Oct 10. Kidney Int. 2024. PMID: 39395628 Free PMC article.
-
Promotion of Colitis in B Cell-Deficient C57BL/6 Mice Infected with Enterotoxigenic Bacteroides fragilis.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Dec 27;25(1):364. doi: 10.3390/ijms25010364. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 38203534 Free PMC article.
-
Prevalence and Characteristics of Plasmid-Encoded Serine Protease EspP in Clinical Shiga Toxin-Producing Escherichia coli Strains from Patients in Sweden.Microorganisms. 2024 Mar 15;12(3):589. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms12030589. Microorganisms. 2024. PMID: 38543640 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

