Design of Motion Detection Device in Sports Based on Deep Learning of Internet of Things
- PMID: 35251145
- PMCID: PMC8890825
- DOI: 10.1155/2022/2613318
Design of Motion Detection Device in Sports Based on Deep Learning of Internet of Things
Retraction in
-
Retracted: Design of Motion Detection Device in Sports Based on Deep Learning of Internet of Things.Comput Intell Neurosci. 2023 Aug 2;2023:9767483. doi: 10.1155/2023/9767483. eCollection 2023. Comput Intell Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 37564575 Free PMC article.
Abstract
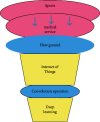
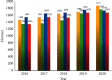
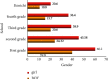
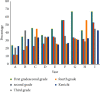
With the improvement of people's income levels in recent years, people have gradually begun to pay more attention to health, and the number of exercise and fitness people has increased year by year. People are gradually willing to pay for sports and fitness, increase sports consumption, and promote the development of the sports and fitness industry. This article aims to study the deep learning based on the Internet of things to make people aware of the importance of sports. Not loving sports is a major problem that contemporary people need to overcome. This article proposes how to design a motion detection device in sports based on deep learning of the Internet of things. Based on the calculation of the economic volume of the deep learning of the Internet of things and the questionnaire survey method, it can be seen that, in today's globalization, although everyone knows the importance of sports, they are unwilling to practice it and would rather spend more time on the Internet. The experimental results of this article show that more than 50% of college students are very interested in sports and fitness, but the actual use is less than 30%, which is not optimistic. In social surveys, this number will be even lower, with only 14% of people interested in sports. Big data is like a "double-edged sword." It not only displays the user's exercise data in front of everyone through the built-in sensors of the mobile phone, but also manages their physical condition through these. How to use the strengths of sports applications at the same time properly disposing of private information is a part of the next development of sports applications that must be faced.
Copyright © 2022 Shaolong Li and Changlei Zhou.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures
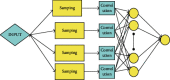
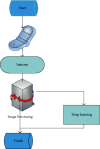

Similar articles
-
Sports Analysis and Action Optimization in Physical Education Teaching Practice Based on Internet of Things Sensor Perception.Comput Intell Neurosci. 2022 Jun 30;2022:7152953. doi: 10.1155/2022/7152953. eCollection 2022. Comput Intell Neurosci. 2022. Retraction in: Comput Intell Neurosci. 2023 Sep 20;2023:9813410. doi: 10.1155/2023/9813410. PMID: 35814534 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
Physical fitness data monitoring of college students based on the internet of things and blockchain.Front Public Health. 2022 Sep 9;10:940451. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2022.940451. eCollection 2022. Front Public Health. 2022. PMID: 36159234 Free PMC article.
-
Simulation of sports training recognition system based on internet of things video behavior analysis.Prev Med. 2023 Aug;173:107611. doi: 10.1016/j.ypmed.2023.107611. Epub 2023 Jul 11. Prev Med. 2023. PMID: 37442210
-
Deep Learning Methods for Space Situational Awareness in Mega-Constellations Satellite-Based Internet of Things Networks.Sensors (Basel). 2022 Dec 23;23(1):124. doi: 10.3390/s23010124. Sensors (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36616722 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Comprehensive Review on Smart Health Care: Applications, Paradigms, and Challenges with Case Studies.Contrast Media Mol Imaging. 2022 Sep 29;2022:4822235. doi: 10.1155/2022/4822235. eCollection 2022. Contrast Media Mol Imaging. 2022. PMID: 36247859 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Retracted: Design of Motion Detection Device in Sports Based on Deep Learning of Internet of Things.Comput Intell Neurosci. 2023 Aug 2;2023:9767483. doi: 10.1155/2023/9767483. eCollection 2023. Comput Intell Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 37564575 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Thomas D. T., Erdman K. A., Burke L. M. Position of the Academy of nutrition and dietetics, dietitians of Canada, and the American college of sports medicine: nutrition and athletic performance. Journal of the Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics . 2016;116(3):501–528. doi: 10.1016/j.jand.2015.12.006. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Hao X., Zhang G., Ma S. Deep learning. International Journal of Semantic Computing . 2016;10(3):417–439. doi: 10.1142/s1793351x16500045. - DOI
-
- Levine S., Pastor P., Krizhevsky A., Julian I., Deirdre Q. Learning hand-eye coordination for robotic grasping with deep learning and large-scale data collection. The International Journal of Robotics Research . 2016;37(4-5):421–436. doi: 10.1177/0278364917710318. - DOI
-
- Song H., Brandt-Pearce M. A 2-D discrete-time model of physical impairments in wavelength-division multiplexing systems. Journal of Lightwave Technology . 2012;30(5):713–726. doi: 10.1109/jlt.2011.2180360. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

