Cell Surface Proteins for Enrichment and In Vitro Characterization of Human Pluripotent Stem Cell-Derived Myogenic Progenitors
- PMID: 35251185
- PMCID: PMC8894063
- DOI: 10.1155/2022/2735414
Cell Surface Proteins for Enrichment and In Vitro Characterization of Human Pluripotent Stem Cell-Derived Myogenic Progenitors
Abstract
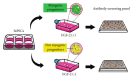
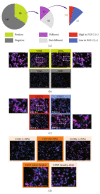
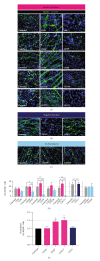
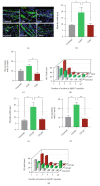
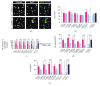
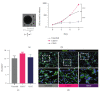
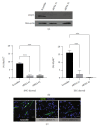
Human myogenic progenitors can be derived from pluripotent stem cells (PSCs) for use in modeling natural and pathological myogenesis, as well as treating muscle diseases. Transgene-free methods of deriving myogenic progenitors from different PSC lines often produce mixed populations that are heterogeneous in myogenic differentiation potential, yet detailed and accurate characterization of human PSC-derived myogenic progenitors remains elusive in the field. The isolation and purification of human PSC-derived myogenic progenitors is thus an important methodological consideration when we investigate the properties and behaviors of these cells in culture. We previously reported a transgene-free, serum-free floating sphere culture method for the derivation of myogenic progenitors from human PSCs. In this study, we first performed comprehensive cell surface protein profiling of the sphere culture cells through the screening of 255 antibodies. Next, we used magnetic activated cell sorting and enriched the cells according to the expression of specific surface markers. The ability of muscle differentiation in the resulting cells was characterized by immunofluorescent labeling and quantification of positively stained cells. Our results revealed that myotube-forming cells resided in the differentiated cultures of CD29+, CD56+, CD271+, and CD15- fractions, while thick and multinucleated myotubes were identified in the differentiated cultures from CD9+ and CD146+ fractions. We found that PAX7 localization to the nucleus correlates with myotube-forming ability in these sorted populations. We also demonstrated that cells in unsorted, CD271+, and CD15- fractions responded differently to cryopreservation and prolonged culture expansion. Lastly, we showed that CD271 expression is essential for terminal differentiation of human PSC-derived myogenic progenitors. Taken together, these cell surface proteins are not only useful markers to identify unique cellular populations in human PSC-derived myogenic progenitors but also functionally important molecules that can provide valuable insight into human myogenesis.
Copyright © 2022 Sin-Ruow Tey et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Derivation of myogenic progenitors directly from human pluripotent stem cells using a sphere-based culture.Stem Cells Transl Med. 2014 May;3(5):564-74. doi: 10.5966/sctm.2013-0143. Epub 2014 Mar 21. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2014. PMID: 24657962 Free PMC article.
-
Efficient Muscle Regeneration by Human PSC-Derived CD82+ ERBB3+ NGFR+ Skeletal Myogenic Progenitors.Cells. 2023 Jan 18;12(3):362. doi: 10.3390/cells12030362. Cells. 2023. PMID: 36766703 Free PMC article.
-
Genomic Safe Harbor Expression of PAX7 for the Generation of Engraftable Myogenic Progenitors.Stem Cell Reports. 2021 Jan 12;16(1):10-19. doi: 10.1016/j.stemcr.2020.11.001. Epub 2020 Dec 3. Stem Cell Reports. 2021. PMID: 33275879 Free PMC article.
-
Generation of human myogenic progenitors from pluripotent stem cells for in vivo regeneration.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2022 Jul 8;79(8):406. doi: 10.1007/s00018-022-04434-8. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2022. PMID: 35802202 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Coding Cell Identity of Human Skeletal Muscle Progenitor Cells Using Cell Surface Markers: Current Status and Remaining Challenges for Characterization and Isolation.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2019 Nov 26;7:284. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2019.00284. eCollection 2019. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2019. PMID: 31828070 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Comprehensive Discovery of the Accessible Primary Amino Group-Containing Segments from Cell Surface Proteins by Fine-Tuning a High-Throughput Biotinylation Method.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Dec 23;24(1):273. doi: 10.3390/ijms24010273. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36613715 Free PMC article.
-
Cellular and transcriptomic changes by the supplementation of aged rat serum in human pluripotent stem cell-derived myogenic progenitors.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2024 Oct 15;12:1481491. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2024.1481491. eCollection 2024. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2024. PMID: 39474351 Free PMC article.
-
Syrah Grape Polyphenol Extracts Protect Human Skeletal Muscle Cells from Oxidative and Metabolic Stress Induced by Excess of Palmitic Acid: Effect of Skin/Seed Ripening Stage.Antioxidants (Basel). 2024 Mar 19;13(3):373. doi: 10.3390/antiox13030373. Antioxidants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38539906 Free PMC article.
-
EpCAM Signaling in Oral Cancer Stem Cells: Implications for Metastasis, Tumorigenicity, and Therapeutic Strategies.Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2025 Feb 14;47(2):123. doi: 10.3390/cimb47020123. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2025. PMID: 39996844 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Gheller B. J., Blum J., Soueid-Baumgarten S., Bender E., Cosgrove B. D., Thalacker-Mercer A. Isolation, culture, characterization, and differentiation of human muscle progenitor cells from the skeletal muscle biopsy procedure. Journal of Visualized Experiments . 2019;150(150) doi: 10.3791/59580. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

