Intravitreal Administration Effect of Adipose-Derived Mesenchymal Stromal Cells Combined with Anti-VEGF Nanocarriers, in a Pharmaceutically Induced Animal Model of Retinal Vein Occlusion
- PMID: 35251186
- PMCID: PMC8890865
- DOI: 10.1155/2022/2760147
Intravitreal Administration Effect of Adipose-Derived Mesenchymal Stromal Cells Combined with Anti-VEGF Nanocarriers, in a Pharmaceutically Induced Animal Model of Retinal Vein Occlusion
Abstract
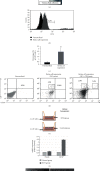
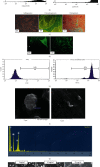
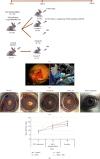
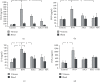
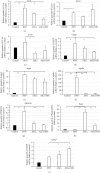
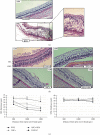
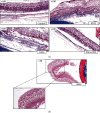
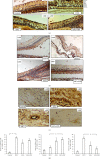
Antiangiogenic therapeutic agents (anti-VEGF) have contributed to the treatment of retinal vein occlusion (RVO) while mesenchymal stromal cell- (MSCs-) mediated therapies limit eye degeneration. The aim of the present study is to determine the effect of adipose-derived MSCs (ASCs) combination with nanocarriers of anti-VEGF in a pharmaceutically induced animal model of RVO. Nanoparticles (NPs) of thiolated chitosan (ThioCHI) with encapsulated anti-VEGF antibody were prepared. ASCs were isolated and genetically modified to secrete the green fluorescence GFP. Twenty-four New Zealand rabbits were divided into the I-IV equal following groups: ASCs, ASCs + nanoThioCHI-anti-VEGF, RVO, and control. For the RVO induction, groups I-III received intravitreal (iv) injections of MEK kinase inhibitor, PD0325901. Twelve days later, therapeutic regiments were administered at groups I-II while groups III-IV received BSS. Two weeks later, the retinal damage evaluated via detailed ophthalmic examinations, histological analysis of fixed retinal sections, ELISA for secreted cytokines in peripheral blood or vitreous fluid, and Q-PCR for the expression of related to the occlusion and inflammatory genes. Mild retinal edema and hemorrhages, limited retinal detachment, and vasculature attenuation were observed in groups I and II compared with the pathological symptoms of group III which presented a totally disorganized retinal structure, following of positive immunostaining for neovascularization and related to RVO markers. Important reduction of the high secreted levels of inflammatory cytokines was quantified in groups I and II vitreous fluid, while the expression of the RVO-related and inflammatory genes has been significantly decreased especially in group II. GFP+ ASCs, capable of being differentiated towards neural progenitors, detected in dissociated retina tissues of group II presenting their attachment to damaged area. Conclusively, a stem cell-based therapy for RVO is proposed, accompanied by sustained release of anti-VEGF, in order to combine the paracrine action of ASCs and the progressive reduction of neovascularization.
Copyright © 2022 Eleni Gounari et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
PD0325901, a mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase inhibitor, produces ocular toxicity in a rabbit animal model of retinal vein occlusion.J Ocul Pharmacol Ther. 2009 Dec;25(6):519-30. doi: 10.1089/jop.2009.0060. J Ocul Pharmacol Ther. 2009. PMID: 19929595
-
Caspase-9 inhibition confers stronger neuronal and vascular protection compared to VEGF neutralization in a mouse model of retinal vein occlusion.Front Neurosci. 2023 Jun 28;17:1209527. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2023.1209527. eCollection 2023. Front Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 37449272 Free PMC article.
-
Creation of Retinal Vein Occlusion Model in Cynomolgus Monkeys and Determination of its Pathological Features.Curr Neurovasc Res. 2021;18(1):123-133. doi: 10.2174/1567202617999200831151118. Curr Neurovasc Res. 2021. PMID: 32867658
-
Optimal Treatment of Retinal Vein Occlusion: Canadian Expert Consensus.Ophthalmologica. 2015;234(1):6-25. doi: 10.1159/000381357. Epub 2015 Jun 12. Ophthalmologica. 2015. PMID: 26088287 Review.
-
Comparison between Ozurdex and intravitreal anti-vascular endothelial growth factor treatment for retinal vein occlusion-related macular edema: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.Indian J Ophthalmol. 2019 Nov;67(11):1800-1809. doi: 10.4103/ijo.IJO_382_19. Indian J Ophthalmol. 2019. PMID: 31638037 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Recent Advances of Adipose-Tissue-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Based Therapy for Retinal Diseases.J Clin Med. 2023 Nov 9;12(22):7015. doi: 10.3390/jcm12227015. J Clin Med. 2023. PMID: 38002628 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Chatziralli I., Nicholson L., Sivaprasad S., Hykin P. Intravitreal steroid and anti-vascular endothelial growth agents for the management of retinal vein occlusion: evidence from randomized trials. Expert Opinion on Biological Therapy . 2015;15(12):1685–1697. doi: 10.1517/14712598.2015.1086744. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

