First-line immunotherapy or angiogenesis inhibitor plus chemotherapy for HER2-altered NSCLC: a retrospective real-world POLISH study
- PMID: 35251321
- PMCID: PMC8894956
- DOI: 10.1177/17588359221082339
First-line immunotherapy or angiogenesis inhibitor plus chemotherapy for HER2-altered NSCLC: a retrospective real-world POLISH study
Abstract
Background: There have been no comprehensive large-scale studies that have evaluated the benefits of chemotherapy-based regimens in addressing HER2-altered advanced non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) in a first-line setting. Data on HER2 alteration subtypes and concomitant alterations are also limited. Accordingly, our retrospective, real-world POLISH study assesses the efficacy of first-line chemotherapy alone (C) as well as combinations with immune checkpoint inhibitors (C + I) or angiogenesis inhibitors (C + A) for HER2-altered NSCLC; molecular features are also reported.
Methods: HER2-altered NSCLC patients who received a first-line treatment between November 2015 and September 2021 were screened. Patients treated with C, C + I, or C + A were included in our final efficacy analysis. Progression-free survival (PFS) was compared between the subgroups. A Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) analysis was performed to evaluate concomitant alterations.
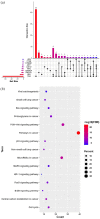
Results: A total of 293 patients were screened, with an identification of HER2 amplification and 37 distinct HER2 mutations, and 210 cases treated with C, C + I, or C + A were ultimately included. C + A achieved longer PFS than C (5.63 vs 4.03 months, hazard ratio: 0.64, 95% confidence interval [CI]: 0.46-0.88, p = 0.006). C + I did not improve median PFS compared to C + A or C (both p > 0.05), despite the programmed cell death ligand-1 (PD-L1) expression or tumor mutational burden. KEGG analysis revealed that concomitant upregulation of PI3 K/AKT pathway signaling was common in HER2-altered NSCLC.
Conclusion: Chemotherapy plus angiogenesis inhibitors may yield a greater survival benefit than chemotherapy alone in a first-line setting for HER2-altered NSCLC, whereas an immune-based combination therapy may not be superior to a sole chemotherapy regimen. Activation of PI3 K/AKT signaling may mediate immunosuppression in HER2-altered NSCLC.
Keywords: HER2 alteration; angiogenesis inhibitor; chemotherapy; immunotherapy; non-small-cell lung cancer; real-world study.
© The Author(s), 2022.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest statement: The authors declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures



References
-
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2020. CA Cancer J Clin 2020; 70: 7–30. - PubMed
-
- NCCN clinical practice guidelines in oncology (NCCN Guidelines®), non-small cell lung cancer. Version 5, 2021. www.nccn.org/patients
-
- Shigematsu H, Takahashi T, Nomura M, et al.. Somatic mutations of the HER2 kinase domain in lung adenocarcinomas. Cancer Res 2005; 65: 1642–1646. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

