Eosinophilic airway diseases: basic science, clinical manifestations and future challenges
- PMID: 35251534
- PMCID: PMC8896196
- DOI: 10.1080/20018525.2022.2040707
Eosinophilic airway diseases: basic science, clinical manifestations and future challenges
Abstract
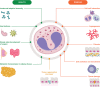
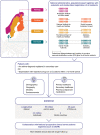
Eosinophils have a broad range of functions, both homeostatic and pathological, mediated through an array of cell surface receptors and specific secretory granules that promote interactions with their microenvironment. Eosinophil development, differentiation, activation, survival and recruitment are closely regulated by a number of type 2 cytokines, including interleukin (IL)-5, the key driver of eosinophilopoiesis. Evidence shows that type 2 inflammation, driven mainly by interleukin (IL)-4, IL-5 and IL-13, plays an important role in the pathophysiology of eosinophilic airway diseases, including asthma, chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps, eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis and hypereosinophilic syndrome. Several biologic therapies have been developed to suppress type 2 inflammation, namely mepolizumab, reslizumab, benralizumab, dupilumab, omalizumab and tezepelumab. While these therapies have been associated with clinical benefits in a range of eosinophilic diseases, their development has highlighted several challenges and directions for future research. These include the need for further information on disease progression and identification of treatable traits, including clinical characteristics or biomarkers that will improve the prediction of treatment response. The Nordic countries have a long tradition of collaboration using patient registries and Nordic asthma registries provide unique opportunities to address these research questions. One example of such a registry is the NORdic Dataset for aSThmA Research (NORDSTAR), a longitudinal population-based dataset containing all 3.3 million individuals with asthma from four Nordic countries (Denmark, Finland, Norway and Sweden). Large-scale, real-world registry data such as those from Nordic countries may provide important information regarding the progression of eosinophilic asthma, in addition to clinical characteristics or biomarkers that could allow targeted treatment and ensure optimal patient outcomes.
Keywords: Eosinophil; NORDSTAR; Nordic; asthma; chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps; eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis; hypereosinophilic syndrome; real-world; registry; severe asthma.
© 2022 The Author(s). Published by Informa UK Limited, trading as Taylor & Francis Group.
Conflict of interest statement
CJ reports personal fees from AstraZeneca, Chiesi Pharma AB, Boehringer Ingelheim, GSK, Novartis, Orion, Sanofi Genzyme and Teva; LB reports lecture fees from AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, Chiesi Pharma AB, GSK, Novartis, Sanofi Genzyme and Teva; LL reports personal fees from AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, Chiesi, GSK, Mundipharma, Novartis, Orion, Sanofi Genzyme and Teva; HK reports personal fees from AstraZeneca, Chiesi Pharma AB, Boehringer Ingelheim, Novartis, Mundipharma, Sanofi Genzyme, GSK and MSD, and non-financial support from AstraZeneca and Orion Pharma; JK has received lecture fees from AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, Chiesi, GSK, Novartis and Orion Pharma, and has participated in advisory boards for AstraZeneca, GSK and Novartis; AA has received lecture fees from AstraZeneca, Berlin Chemie Menarini, Boehringer Ingelheim, Chiesi, GSK, MSD, Norameda, Sanofi and Zentiva, support for meeting attendance from AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, Novartis, GSK, Sanofi and Teva, and has participated in advisory boards for AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, GSK, Novartis, Sanofi and Teva; VY reports lecture fees from GSK and Sanofi and has participated in advisory boards for AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, Chiesi and GSK; BA reports speaker honorarium and/or honorarium for advisory board participation from GSK, AstraZeneca, Chiesi, Boehringer Ingelheim, Novartis and Sanofi-Aventis; MR reports lecture fees from GSK; JH reports lecture fees from AstraZeneca, GSK, MEDA, Schering Plough and MSD, and advisory board participation for GSK, Schering Plough and MEDA; ML and PHH are employees of GSK and own stocks/shares; CP reports personal fees and research grants from AstraZeneca, Chiesi Pharma AB, GSK, Novartis, Sanofi Genzyme and Teva.
Figures

References
-
- Maret-Ouda J, Tao W, Wahlin K, et al. Nordic registry-based cohort studies: possibilities and pitfalls when combining Nordic registry data. Scand J Public Health. 2017;45(17_suppl):14–19. - PubMed
-
- Samitas K, Radinger M, Bossios A. Current update on eosinophilic lung diseases and anti-IL-5 treatment. Recent Pat Antiinfect Drug Discov. 2011;6(3):189–205. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
