A Retrospective, Observational, EMR-Based Real-World Evidence Study to Assess the Incidence of Pedal Edema in Essential Hypertensive Patients on Amlodipine or Cilnidipine
- PMID: 35251710
- PMCID: PMC8890895
- DOI: 10.1155/2022/6868143
A Retrospective, Observational, EMR-Based Real-World Evidence Study to Assess the Incidence of Pedal Edema in Essential Hypertensive Patients on Amlodipine or Cilnidipine
Abstract
Introduction: Calcium channel blockers have pedal edema as one of the confining factors of treatment. A real-world study may help evident reality of the situation in regular Indian clinical practice. The aim of the study is to assess effectiveness and incidence of pedal edema in essential hypertensive patients treated with amlodipine or cilnidipine monotherapy.
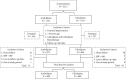
Methods: Retrospective EMR data of adult essential hypertensive patients, prescribed amlodipine (n = 800) or cilnidipine (n = 800) as monotherapy, were analyzed. Incidence of pedal edema from baseline visit was analyzed in terms of dose and duration of treatment. The changes in systolic (SBP) and diastolic blood pressure (DBP) from baseline and proportion of patients achieving target BP goals were assessed.
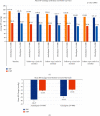
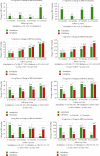
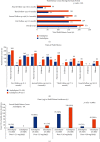
Results: In amlodipine and cilnidipine groups, mean changes in SBP and DBP from baseline to end of the study period were 28.4 and 15.1 mmHg and 24.3 and 13.5 mmHg, respectively (p value <0.05). More than 50% of patients in both groups achieved BP goal at the end of the study (p value 0.266). In amlodipine group, total 23.9% reported pedal edema, while in cilnidipine, 27.6% (p value 0.0863). At the end of the study, 3.5% and 8.2% of patients remain with pedal edema, respectively, in both groups (pvalue <0.005).
Conclusion: Amlodipine demonstrated greater BP reduction at a lower average dose, better efficacy, and tolerability in terms of pedal edema count as a lesser number of patients reported edema at the end of the study and a higher percentage of patients continued the prescribed baseline dosage regimen as compared to cilnidipine. Thus, the study established amlodipine as an effective and well-tolerated antihypertensive for Indians.
Copyright © 2022 Jamshed Dalal et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors, Dr. J. Dalal, Dr. J. P. Sawhney, Dr. P. B. Jayagopal, and Dr. P. K. Hazra, are the advisory board members for Dr. Reddy's Laboratories, Ltd. Dr. Md. Y. Khan, Dr. K. Gaurav, Colette Pinto, and Dr. A. Mane declare that they work in the Medical Affairs Department in Dr. Reddy's Laboratories, Ltd., Hyderabad, India. Dr. S. Rao and Dr. M. Jain declare that there are no conflicts of interest towards publishing the work as the manuscript.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Comparison of amlodipine with cilnidipine on antihypertensive efficacy and incidence of pedal edema in mild to moderate hypertensive individuals: A prospective study.J Adv Pharm Technol Res. 2015 Apr-Jun;6(2):81-5. doi: 10.4103/2231-4040.154543. J Adv Pharm Technol Res. 2015. PMID: 25878978 Free PMC article.
-
Effectiveness and Effect on Renal Parameters of Amlodipine vs. Other Dihydropyridine Calcium Channel Blockers in Patients with Essential Hypertension: Retrospective Observational Study Based on Real-World Evidence from Electronic Medical Records.Cardiol Ther. 2021 Dec;10(2):465-480. doi: 10.1007/s40119-021-00224-8. Epub 2021 Jun 11. Cardiol Ther. 2021. PMID: 34115326 Free PMC article.
-
Cilnidipine for Amlodipine Induced Pedal Edema and its Anti-hypertensive Effect in a Tertiary Care Teaching Hospital of Western Nepal.J Nepal Health Res Counc. 2021 Dec 15;19(3):618-621. doi: 10.33314/jnhrc.v19i3.3583. J Nepal Health Res Counc. 2021. PMID: 35140441
-
Review: a single-pill combination of telmisartan plus amlodipine for the treatment of hypertension.Postgrad Med. 2011 Nov;123(6):58-65. doi: 10.3810/pgm.2011.11.2495. Postgrad Med. 2011. PMID: 22104454 Review.
-
Efficacy of Cilnidipine (L/N-type Calcium Channel Blocker) in Treatment of Hypertension: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized and Non-randomized Controlled Trials.Cureus. 2021 Nov 22;13(11):e19822. doi: 10.7759/cureus.19822. eCollection 2021 Nov. Cureus. 2021. PMID: 34963839 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Retrospective Electronic Medical Records Study to Understand the Usage Patterns and Patient Profiles of Those Prescribed Amlodipine and Its Combinations.Cureus. 2025 Jul 29;17(7):e88954. doi: 10.7759/cureus.88954. eCollection 2025 Jul. Cureus. 2025. PMID: 40896048 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ministry of Health and Family Welfare. District Level Household and Facility Survey . Mumbai, India: Ministry of Health and Family Welfare; 2020. https://data.gov.in/resources/hypertension-age-18-years-and-above-dlhs-iv .
-
- Ministry of Health and Family Welfare. National Family Health Survey . Mumbai, India: Ministry of Health and Family Welfare; 2020. https://rchiips.org/nfhs/abt.html .
-
- GBD 2016 Risk Factors Collaborators. Global, regional, and national comparative risk assessment of 84 behavioral, environmental and occupational, and metabolic risks or clusters of risks, 1990-2016: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2016. Lancet . 2017;392:1345–1422. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(18)32225-6. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation. Global Burden of Diseases Study 2016 . Seattle, WA, USA: Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation; 2020. https://ghdx.healthdata.org/gbd-results-tool .
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

