Lactococcus lactis secreting phage lysins as a potential antimicrobial against multi-drug resistant Staphylococcus aureus
- PMID: 35251775
- PMCID: PMC8896023
- DOI: 10.7717/peerj.12648
Lactococcus lactis secreting phage lysins as a potential antimicrobial against multi-drug resistant Staphylococcus aureus
Abstract
Background: Staphylococcus aureus is an opportunistic Gram-positive bacterium that can form biofilm and become resistant to many types of antibiotics. The treatment of multi-drug resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MDRSA) infection is difficult since it possesses multiple antibiotic-resistant mechanisms. Endolysin and virion-associated peptidoglycan hydrolases (VAPGH) enzymes from bacteriophage have been identified as potential alternative antimicrobial agents. This study aimed to assess the ability of Lactococcus lactis NZ9000 secreting endolysin and VAPGH from S. aureus bacteriophage 88 to inhibit the growth of S. aureus PS 88, a MDRSA.
Method: Endolysin and VAPGH genes were cloned and expressed in L. lactis NZ9000 after fusion with the SPK1 signal peptide for secretion. The recombinant proteins were expressed and purified, then analyzed for antimicrobial activity using plate assay and turbidity reduction assay. In addition, the spent media of the recombinant lactococcal culture was analyzed for its ability to inhibit the growth of the S. aureus PS 88.
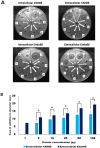
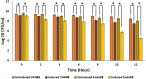
Results: Extracellular recombinant endolysin (Endo88) and VAPGH (VAH88) was successfully expressed and secreted from L. lactis which was able to inhibit S. aureus PS 88, as shown by halozone formation on plate assays as well as inhibition of growth in the turbidity reduction assay. Moreover, it was observed that the spent media from L. lactis NZ9000 expressing Endo88 and VAH88 reduced the viability of PS 88 by up to 3.5-log reduction with Endo88 being more efficacious than VAH88. In addition, Endo88 was able to lyse all MRSA strains tested and Staphylococcus epidermidis but not the other bacteria while VAH88 could only lyse S. aureus PS 88.
Conclusion: Recombinant L. lactisNZ9000 expressing phage 88 endolysin may be potentially developed into a new antimicrobial agent for the treatment of MDRSA infection.
Keywords: Bacteriophage; Endolysin; Lactococcus lactis; Multi-drug resistant Staphylococcus aureus; Virion associated peptidoglycan hydrolase.
©2022 Chandran et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare there are no competing interests.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Novel recombinant endolysin ointment with broad antimicrobial activity against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus isolated from wounds and burns.Arch Microbiol. 2023 Mar 4;205(4):104. doi: 10.1007/s00203-023-03434-x. Arch Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 36869962
-
A Novel Chimeric Endolysin with Antibacterial Activity against Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2017 Jun 30;7:290. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2017.00290. eCollection 2017. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2017. PMID: 28713777 Free PMC article.
-
Enhanced staphylolytic activity of the Staphylococcus aureus bacteriophage vB_SauS-phiIPLA88 HydH5 virion-associated peptidoglycan hydrolase: fusions, deletions, and synergy with LysH5.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2012 Apr;78(7):2241-8. doi: 10.1128/AEM.07621-11. Epub 2012 Jan 20. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2012. PMID: 22267667 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of a Bacteriophage-Derived Murein Peptidase for Elimination of Antibiotic-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus.Curr Protein Pept Sci. 2016;17(2):183-90. doi: 10.2174/1389203716666151102105515. Curr Protein Pept Sci. 2016. PMID: 26521950 Review.
-
Recombinant bacteriophage lysins as antibacterials.Bioeng Bugs. 2010 Jan-Feb;1(1):9-16. doi: 10.4161/bbug.1.1.9818. Bioeng Bugs. 2010. PMID: 21327123 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Heterologous expression and purification of the phage lysin-like bacteriocin LysL from Lactococcus lactis LAC460.FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2024 Jan 9;371:fnae065. doi: 10.1093/femsle/fnae065. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2024. PMID: 39153967 Free PMC article.
-
Phage-Derived Endolysins Against Resistant Staphylococcus spp.: A Review of Features, Antibacterial Activities, and Recent Applications.Infect Dis Ther. 2025 Jan;14(1):13-57. doi: 10.1007/s40121-024-01069-z. Epub 2024 Nov 16. Infect Dis Ther. 2025. PMID: 39549153 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Phage lysins for intestinal microbiome modulation: current challenges and enabling techniques.Gut Microbes. 2024 Jan-Dec;16(1):2387144. doi: 10.1080/19490976.2024.2387144. Epub 2024 Aug 6. Gut Microbes. 2024. PMID: 39106212 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Applications of tandem mass spectrometry (MS/MS) in antimicrobial peptides field: Current state and new applications.Heliyon. 2024 Mar 31;10(7):e28484. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e28484. eCollection 2024 Apr 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 38601527 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cloning, recombinant expression, purification, and functional characterization of AGAAN antibacterial peptide.3 Biotech. 2023 Mar;13(3):88. doi: 10.1007/s13205-023-03512-3. Epub 2023 Feb 18. 3 Biotech. 2023. PMID: 36811032 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Baradaran A, Sieo CC, Foo HL, Illias RM, Yusoff K, Rahim RA. Cloning and in silico characterization of two signal peptides from Pediococcus pentosaceus and their function for the secretion of heterologous protein in Lactococcus lactis. Biotechnology Letters. 2013;35(2):233–238. doi: 10.1007/s10529-012-1059-4. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

